Divergent Plate Tectonics: Boundaries that Pull Apart
Beneath the oceans, lava erupts every day from mid-oceanic ridges. These divergent plate boundaries pull apart from each other creating new igneous rock.
Beneath the oceans, lava erupts every day from mid-oceanic ridges. These divergent plate boundaries pull apart from each other creating new igneous rock.
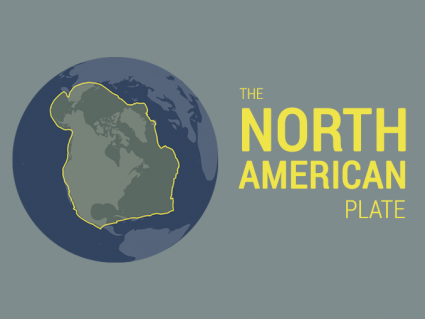
The North American plate extends all the way over the North pole to Siberia. It also includes Greenland, Cuba, the Bahamas and part of the Atlantic Ocean.
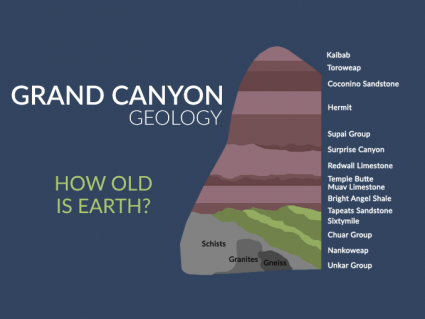
Like a stack of pancakes, younger rock layers pile on top of older layers. We use the law of superposition to reveal Earth’s age and Grand Canyon geology.
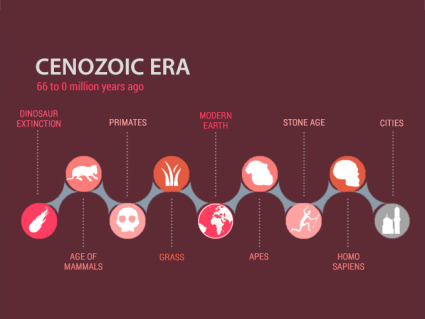
The Cenozoic Era started with the extinction of dinosaurs and moved into the age of mammals.This led to the diversification and increase in size of mammals.

At the end of the Hadean Eon, the Earth was in the late bombardment stage. Earth and the entire solar system was pelted by asteroids, comets and objects.

If you went 200 million years back in time, Earth was 1 supercontinent. Now, it’s made up of 7 separate continents. This is the supercontinent cycle at work.
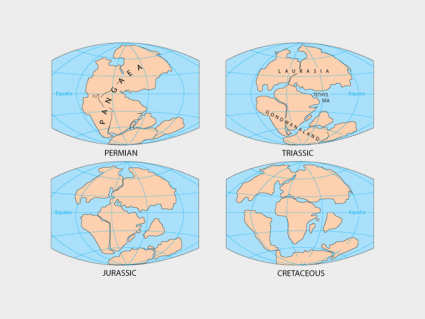
About 200 million years ago, all the continents were together as one giant supercontinent known as Pangaea. Over time, these continents have broken apart.
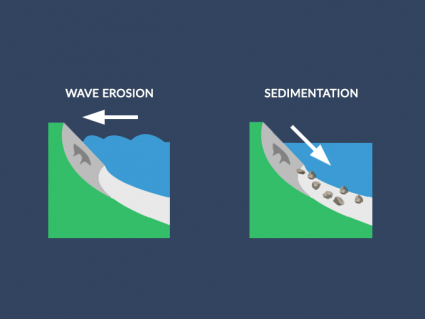
From the remarkable process of plates colliding and building mountains. They are only to be dismantled by mass wasting (weathering, erosion and transport).
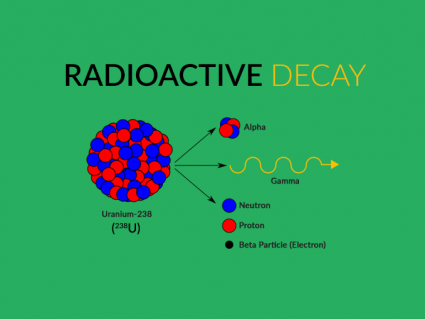
Four radioactive isotopes inside Earth account for 50% of its internal heat. Like a slow cooker, they slowly release heat within the planet keeping it warm.
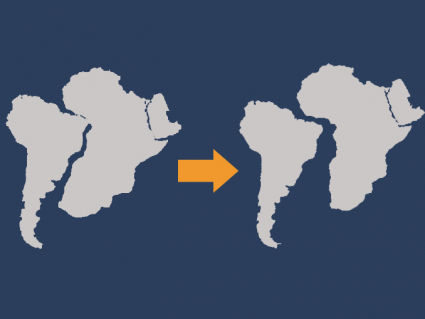
Plate tectonics are deceptively slow. It’s just centimeters each year. Continental drift is the idea that continents passively move due to tectonic activity
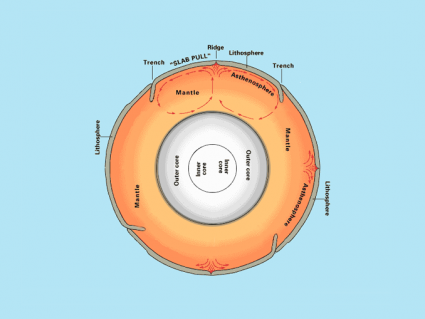
Under the rigid layer of rock we live on, the Earth is plastic & more dense. Because of its fluid properties, mantle convection can occur within the Earth.
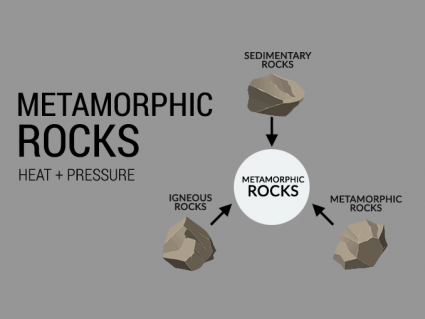
If you take an existing rock and add immense heat or pressure to it, the rock becomes soft and pliable like cookie dough transforming into metamorphic rocks.

Antarctic plate holds the continent of Antarctica including the surrounding ocean. It shares borders with the African, Pacific & South American plate.

Like a rake scraping the dirt, glaciers leave a lasting impression on the land. They can erode mountains, transport vast amount of rock and reshape the land.

Hydrocarbons, oil and coal formation in general are made from living organisms that have been compacted from intense heat and pressure millions of years ago.