Solar Radiation: How Sunlight Heats the Planet

What is solar radiation?
Our sun is 99% of the total mass of the solar system. It’s this healthy dose of solar energy that heats up our planet.
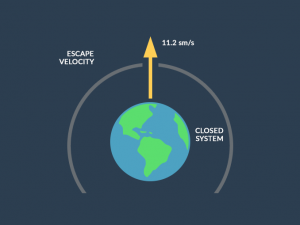
The balance of Earth’s temperature relies on how much energy enters and leaves the planet’s system.
- ABSORPTION: When incoming energy from the sun is absorbed by the Earth system, Earth warms.
- REFLECTION: If the sun’s energy is reflected back into space, Earth avoids warming.
When absorbed energy is released back into space, Earth cools. Natural and human causes can influence Earth’s energy balance.
How does the sun heat our planet?
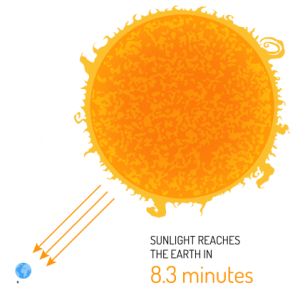
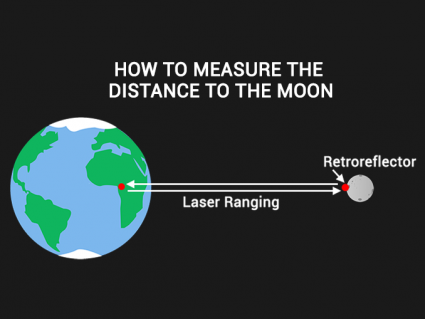
Fusion reactions power the sun. It takes sunlight 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach us. This is the solar radiation that heats our planet.
The sun is 1 astronomical unit to reach us. Because Earth is in the Goldilocks zone, we receive the right amount of heat to harbor life.
By providing a healthy portion of UV rays, plants use it for photosynthesis. Without sunlight, you cut plants off from the energy needed for photosynthesis.
How does it relate to the greenhouse effect?
Earth relies on solar radiation to heat the planet. Overall, it depends on how much energy enters and leaves the planet’s system.
When the sun’s energy is reflected back into space, Earth avoids warming. By releasing solar radiation back into space, Earth cools.
When incoming energy from the sun is absorbed by the Earth system, Earth warms. The greenhouse effect increases warming by acting like a lid on a container.
Like a sealed plastic container, greenhouse gases can keep heat trapped in. For example, sources of air pollution include carbon dioxide, methane, and CFCs.
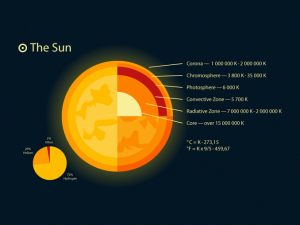
What is a fusion reaction from the sun?
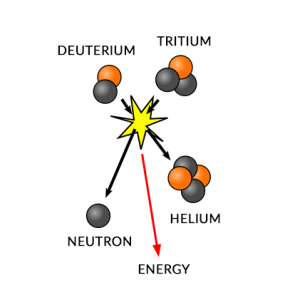
If you look at the composition of the sun, it’s mostly hydrogen and helium. Stars like our sun undergo thermonuclear reactions where four hydrogen atoms combine into helium through heat.
According to Einstein, you can’t lose mass. But you can convert mass to energy. So all stars do during their life cycle is just burn hydrogen into helium and release energy.
Typically, main sequence stars like the sun go through this process for about 95% of their life.
“Eventually, all fires burn out. Our sun has a life expectancy of about 10 billion years. Currently, we’re into year 5 billion years of our Sun’s lifespan.”