5 Facts About the Sun [Infographic]

Facts About the Sun
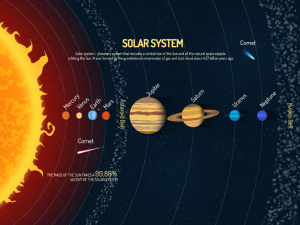
The sun is at the center of our solar system. And it’s so massive that it holds 99.9% of the total mass of the solar system. That means that nearly 1300 Jupiters can fit the sun!
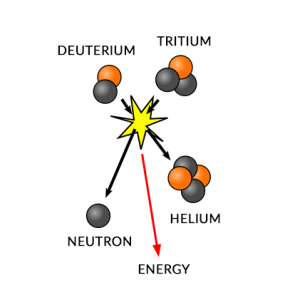
By fusing hydrogen into helium, the sun releases vast amounts of energy as sunlight toward Earth.
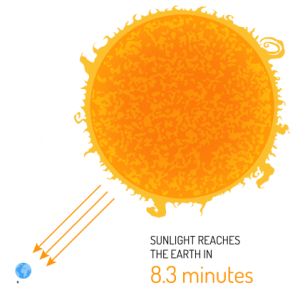
It takes light 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach us. It’s this solar energy that heats the Earth.
But how did the sun come into existence? And how much longer will the sun’s fire burn for? Find out more with these 5 facts about the sun.
1. The size of the sun is ginormous
The sun is at the center of our solar system. And it’s so massive that it holds 99.9% of the total mass of the solar system.
You’d need 1.3 million Earths to fill up the Sun. Or it would take nearly 1300 Jupiters to fit the sun!
Here’s a video of the relative size of the Earth compared to the sun.
2. The sun shines a healthy dose of solar radiation
Fusion reactions power the sun. The sun fuses hydrogen to helium releasing vast amounts of energy.
It takes light 1 astronomical unit to reach us. It’s because of this solar energy that Earth is the only planet known to harbor life.
By providing a healthy portion of UV rays, plants use it for photosynthesis. Without sunlight, you cut plants off from the energy needed for photosynthesis.
The balance of Earth’s temperature relies on how much energy enters and leaves the planet’s system. When incoming energy from the sun is absorbed by the Earth system, Earth warms. The greenhouse effect increases warming further.
When the sun’s energy is reflected back into space, Earth avoids warming. When absorbed energy is released back into space, Earth cools.
3. The sun is 99.9% of the mass in the solar system
The sun is so massive that it gathers up 99.9% of gas and dust in the solar system. Solar wind swept in hydrogen and helium closer to the sun because these particles were smaller in size.
The sun left just enough behind for gravity to build up other things like planets and moons. For example, heavier elements like iron and zinc coalesced to the core of Earth.
According to Einstein, you can’t lose mass. But you can convert mass to energy. Stars undergo thermonuclear reactions where four hydrogen atoms are combined together into helium through heat.
So all stars do during their life cycle is just burn hydrogen into helium and release energy. Typically, main sequence stars like the sun go through this process for about 95% of their life.
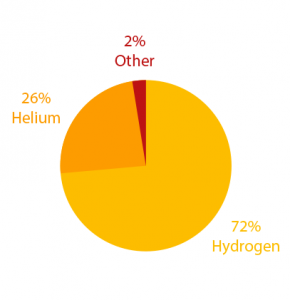
4. It’s mostly hydrogen and helium
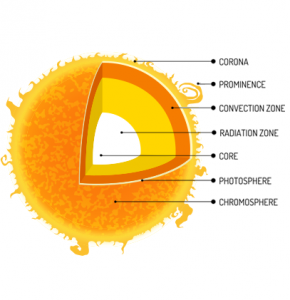
The sun’s layers include the corona, chromosphere, photosphere, convection zone, radiative zone, and core. It’s also composed of 72% hydrogen, 26% helium and 2% other gases.
- Corona – 1,000,000 K to 2,000,000 K
- Chromosphere – 3,800 K to 35,000 K
- Photosphere – 6,000 K
- Convection Zone – 5,700 K
- Radiative Zone – 7,000,000 K to 2,000,000 K
- Core – Over 15,000,000 K
The corona extends millions of kilometers out into space. This fiery halo of charged particles can reach temperatures of 2,000,000 K.
The corona produces solar wind which is a flood of plasma that streams out of the sun and across the solar system. During major disturbances, solar winds can disrupt orbiting satellites.
5. The sun will burn out in about 4 billion years
The sun is a main sequence star meaning for 95% of its life, it releases energy through thermonuclear reactions. Just like any fire, eventually, it burns out. Similarly, stars all have lifetimes. Heavyweight stars have the most fuel. But burns it at the fastest rate.
The smallest stars live the longest at a minimum of 50 billion years. If you compare this to the universe, it’s only 13 billion years old. That means that the lifespan of a star is longer than the creation of our universe up to this point.
Our sun is 1 solar mass (SM) and is classified as lightweight. In the lightweight category, this means that it has a life expectancy of about 10 billion years.
“Contributing makes me feel like I’m being useful to the planetCurrently, we’re into 5 billion years for our sun. It’s at the middle age of its life and has about 4 billion more years. Unlike red supergiants, our sun won’t become a supernova and will collapse into a white dwarf.”
Quick facts about the sun
From its age to its temperature, here are some quick facts about the sun.
- Age: 4.6 billion years
- Type: Yellow Dwarf (G2V)
- Diameter: 1,392,684 km
- Equatorial: 4,370,005.6 km
- Mass:199 x 1030 kg (333,060 Earths)
- Core temperature: 13,599,726°C
- Surface temperature: 5,500°C
- The mass of the sun takes 99.86% weight of the solar system.
- It takes 8.3 minutes for sunlight to reach the Earth.
- The average distance from the Earth to the sun is 149.6 million kilometers.
- The sun is mostly Hydrogen (74%), Helium (24%) and other elements
- Composition of the sun: corona, prominence, convection zone, radiation zone, core, photosphere and chromosphere