Main Sequence Star: Our Sun’s Thermonuclear Reaction
Main Sequence Stars
The sun is so massive that it’s 99.9% of the mass in our solar system. But there was just enough behind for gravity to build up other things like our planet.
Main sequence stars are the most common type of stars in the universe and are characterized by their stable fusion of hydrogen into helium in their cores.
But how did the sun come into existence? And how much longer will the sun’s fire burn for? Read on to find out more.
How did the sun come into existence?
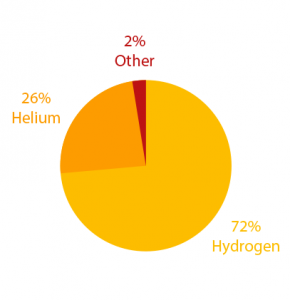
The sun is mostly hydrogen (74%) and helium (25%). It started with hydrogen bundling together and rotating.
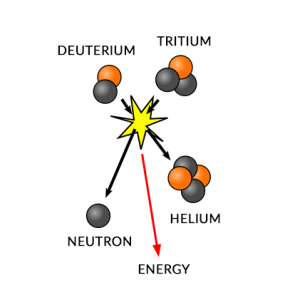
Eventually, four hydrogen atoms connect with four electrons to create one helium atom through heat.
If you look at hydrogen on the periodic table, four individual hydrogen atoms have more mass than one helium atom.
According to Einstein, you can’t lose mass. But you can convert mass to energy. Stars are a thermonuclear reaction where four hydrogen atoms are put together into helium.
What is a main sequence star?
In our case, our Sun releases the energy that we see as sunlight on Earth. So, it burns hydrogen into helium and releases energy.
Typically, stars go through this “main sequence” for about 95% of its life. So for most of our sun’s life, it releases energy as sunlight through thermonuclear reactions.
During this extended main sequence phase, stars like our Sun maintain a delicate balance between the inward gravitational force and the outward pressure generated by nuclear fusion, making them stable sources of energy for a considerable portion of their existence.
How much longer will the sun’s fire burn?
Just like any fire, eventually fires burn out. Similarly, stars all have life spans. Heavyweight stars have the most fuel but burn it at the fastest rate.
The smallest stars live the longest at a minimum of 50 billion years. If you compare this to the universe, it’s only 13 billion years old.
Our Sun is 1 SM and is classified as lightweight. In the lightweight category, this means that it has a life expectancy of about 10 billion years.
Currently, we’re into 5 billion years for our Sun. It’s at the middle age of its life and has about 4 billion more years. It won’t become a supernova and will collapse into a white dwarf.
Other quick facts about the sun
- Age: 4.6 billion years
- Type: Yellow Dwarf (G2V)
- Diameter: 1,392,684 km
- Equatorial: 4,370,005.6 km
- Mass: 199 x 1030 kg (333,060 Earths)
- Core temperature: 13,599,726°C
- Surface temperature: 5,500°C
- The mass of the sun takes 99.86% weight of the solar system.
- It takes 8.3 minutes for sunlight to reach the Earth.
- The average distance from the Earth to the sun is 149.6 million kilometers.
- The sun is mostly Hydrogen (74%), Helium (24%), Carbon (15%), Other
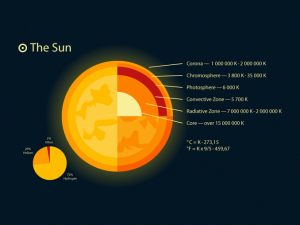
- Composition of the Sun: Corona, Prominence, Convection Zone, Radiation Zone, Core, Photosphere, and Chromosphere