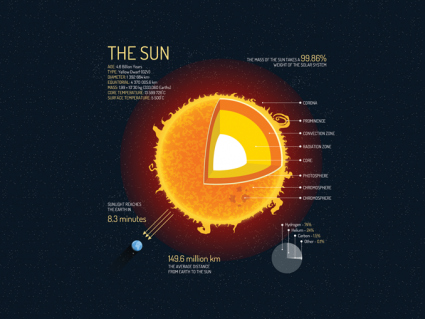
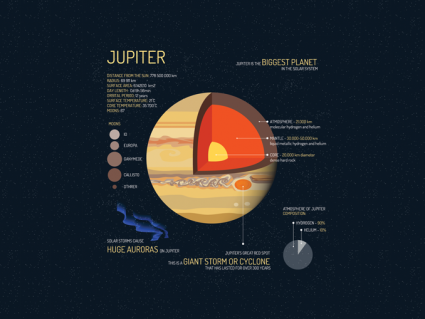
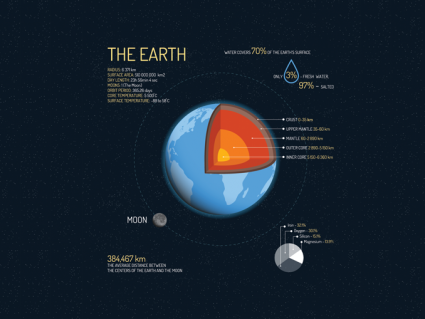
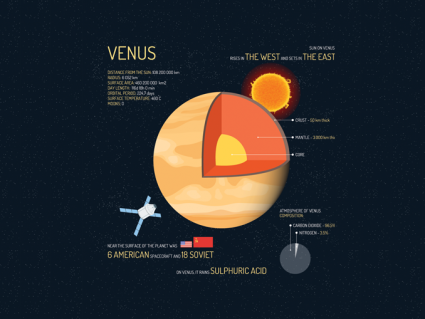
How To Define the Geosphere

What is the Geosphere?
It’s difficult to pinpoint an exact definition for the “geosphere” because it’s used in several different ways:
- COMMON DEFINITION: The common dictionary definition is that it’s simply just the solid outer shell and inner crust of Earth.
- USGS: But the USGS coined the term of the geosphere a bit differently. They define it as the interaction between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere.
Let’s take a look at both definitions and which one we should consider using in Earth Science.
USGS’s definition of “geosphere”
The USGS definition of geosphere considers how the biosphere (living organisms) interacts with the hydrosphere (liquid water), lithosphere (solid rocks), cryosphere (frozen ice), and atmosphere (gas envelope).
Specifically, it emphasizes the flux of energy in an environment. Also, it takes a bit more of a holistic approach by including several spheres of Earth.
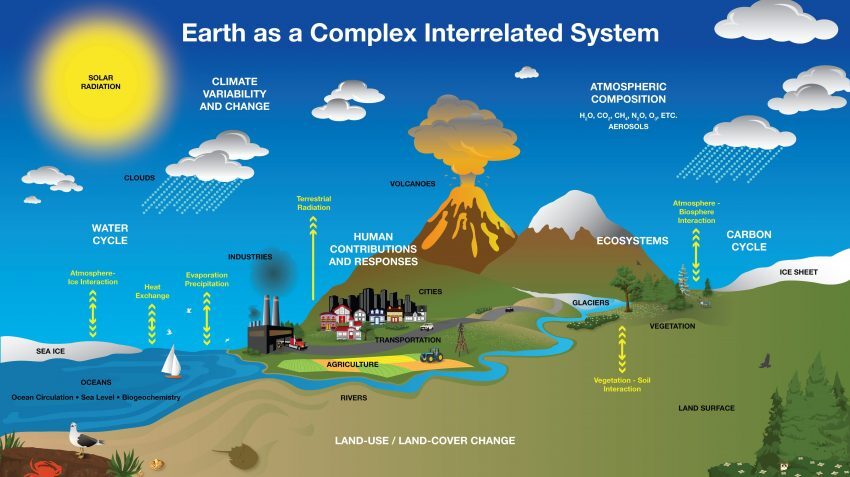
For example, plants grow using carbon dioxide from the air. But they also absorb water from the hydrosphere and spread their roots in the soil (pedosphere). This way of defining the geosphere takes into account the whole picture of the “Earth itself”.
I prefer this definition of geosphere because it focuses on the interaction between elements in nature. It’s not just the physical aspects of our planet. But it includes the interaction of life.
The dictionary definition of the geosphere
The other definition of the geosphere is that it only consists of Earth’s rocks, minerals, and mantle. The origin of this definition is what you commonly find in dictionaries and textbooks.
For example, it includes oceanic/continental crust and plate tectonics. But it doesn’t consider other aspects of an environment such as air, water, ice, or living organisms.
This definition of geosphere just takes into account the rigid sphere that makes up our planet. The reason I prefer it less is that it has significant overlap with an existing earth science term “lithosphere”.
If you want to define the lithosphere, it consists of Earth’s hard, rigid outer shell. And this definition basically matches the geosphere, which is any of the solid Earth.
How To Define the Geosphere
The common definition of geosphere is that it’s just the outer shell and inner crust of Earth.
But the alternative definition is that it’s not only rocks, soil, and mantle. Instead, it also includes water, ice, air, and how it interacts with life.
Back to the term “geosphere”… In Latin, “geo” means “Earth”.
So shouldn’t the definition of geosphere incorporate all of Earth’s spheres? What do you think? Which definition of geosphere do you prefer? Let us know with a comment below.