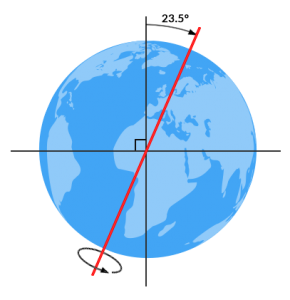
Earth Tilt: 23.5 Degrees Axis

“If you stick a pencil directly through the Earth at the point of rotation, these two points are the north and south poles. Now if you twist your wrist at 23.5°, this is the Earth tilt.”
The Earth tilt is a fundamental and dynamic feature that significantly influences our planet’s climate, weather patterns, and the natural rhythms of life.
This axial tilt, which currently stands at approximately 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the Sun, is responsible for the changing seasons, the variation in day length, and the distribution of sunlight across different latitudes.
All of this plays pivotal roles in shaping Earth’s ecosystems and the behavior of living organisms.
Today, we’re going to explore our planet’s tilt in more detail.
What causes seasonal patterns?
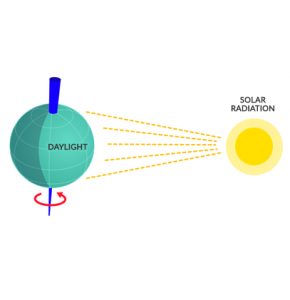
Because the Earth is tilted on its axis, it’s the main reason why we have seasons.
- SUMMER: As the Earth revolves around the sun, the hemisphere that’s tilted towards the sun receives the most sunlight. When it receives more sunlight, this is summertime.
- WINTER: The hemisphere that’s tilted away from the sun receives less sunlight, and has shorter days. As a result, it becomes colder and this is the winter season.
- 24-HOUR DARKNESS: At the North Pole, it’s possible to have 24-hour days in darkness because of the tilt of the Earth.
At the equator, it’s exposed to sunlight more often. This is why is much hotter at the equator year-round. Because it is hotter for longer periods of time, there is less difference between seasons.
Why is the north and south pole so cold?
At the equator, the sun hits the Earth directly. Whereas at the poles, the sun’s rays can barely touch it.
More specifically, it’s not because the equator is closer to the sun. But it’s because the sun is directly shining on the equator.
This is why Earth has the warmest ecosystems at the equator like tropical rainforests and deserts.
“The north and south pole hardly receive any heat from the sun’s rays. This creates the coldest places on Earth like tundras and polar deserts.”
How did the moon’s impact change Earth’s tilt?
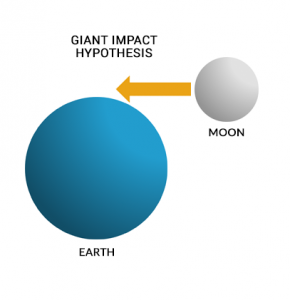
Long ago, the moon collided with Earth. It was a glancing blow impact and not a head-on collision. The giant impact hypothesis describes the time when Earth first met the moon.
Since then, the moon has been a close companion orbiting the Earth.
This giant impact had profound effects on Earth. For example, it tilted Earth on its axis promptly giving it seasons.
In tandem, they control ocean tides, slow rotational speed, and stabilize Earth from wobbling.







sea shore wind speed is more, is it only due 23 degree tilt of earth rotation ??
my answer is mst ( mass x specified heat x Time) of Sea water and land is different which creates change of temperature above Sea level and land ., which creates difference of air pressure, hence wind will flow from sea to land.thus the reason of waves.
Actually, the Giant Impact Hypothesis states that it wasn’t the Moon that collided with our Earth, but Theia (a protoplanet of a size similar to Mars). This happened when the Earth was a very young planet – about 4.5 billion years ago. The impact was so huge, that it tilted our planet, but also destroyed Theia and send its pieces and Earth’s pieces out into the space. Whose pieces eventually joined together into a disk of mostly vapor and molten rock. Eventually, the disk started to cool off and solidify, until it became our Moon. That’s why the Moon’s rocks have similar characteristics to the Earth’s rocks, but strong influence of Thea’s rocks has been preserved in our Moon as well. Moon also does not have the iron core, the Earth does, but, instead, its center is composed of the same material as the rest of the Moon.
I think I can see where the moon or an extremely large asteroid impacted the earth and most likely caused the tilt. Are you interested? Once you see it you can’t unsee it!
I can explain another way we can get seasonal weather and the longest and shortest days of the year, without the planet being tilted. Google Earth Science Novato. I welcome the debate.
How fast does the earth tilt back and forth, from season to season?
Does the earth tilt 23.5 happen gradually?
Has the axes changed the way Florida gets hit by hurricane
This was very helpful thank you
Yes, it does hit one pole more than the other. It’s why some places close to the north pole can have 24-hour sunlight as well.
With the tilt should not the sun be hitting more on one pole? And if earth travels around the sun, should not the sun be hitting the same place on full circle?
Wow
Earth’s tilt does vary between 22.1° to 24.5° and takes 40,000 years to complete as part of the Milankovitch Cycle.
Here’s more on that phenomenon – https://earthhow.com/milankovitch-cycle/
If the earth for whatever reason(is this possible?)has tilted to 24 degrees would this cause global warming? Could the aadditional tilt of a lesser degree cause G.W.? Just curios!
The visual cue that the earth is rotating towards the east is the sun rising in the east and moving towards the west. But what is the visual cue that the earth is revolving around the sun in a clockwise or counter-clockwise direction?
Chris Hughes
Is it my imagination, or has the earths tilt changed? The Sun seems to be higher at noon than usual.