Earth Rotation: The Day-Night Boundary
Get the spin on Earth’s rotation
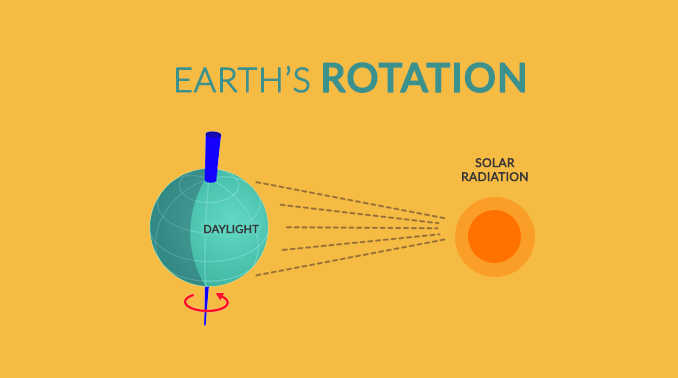
Not only is the Earth revolving around the sun, but the Earth is also spinning.
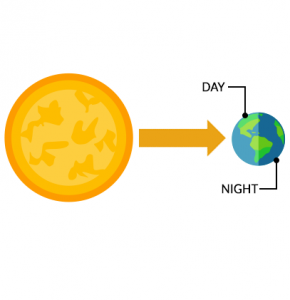
As the Earth spins, the sun always shines on one side which gives it sunlight. When you’re facing the sun, it’s daytime.
But when you’re on the part of the Earth that’s away from the sun, it’s nighttime.
So, we have day and night because of the Earth’s rotation. And that line that separates day from night is the terminator line.
How long is a full rotation on Earth?
A full day on Earth is clocked at 23h 56min 4sec. That’s a bit less than 24 hours.
In order to make a complete rotation in this amount of time, Earth spins at 1000 miles per hour (1600 km/hr).
That makes Earth’s rotation faster than a bullet train. But we’re so used to it that we don’t feel its tremendous rotational speed. Earth rotation is a pace-setter for our sleep patterns.
“If you shine a flashlight on a spinning top, the side lit up is daytime. The dark side is night time. That’s how our day-night cycles work with the sun as our flashlight.”
What are atomic clocks?
Every day, the Earth rotates a full 360 degrees. More specifically, it takes about 24 hours to fully spin in a circle. Clocks and time are set to this rotation
When the Earth spins on its axis, our clocks are set for this duration of time. For example, our hours, minutes, and seconds are tied to the length of a day.
Because the Earth’s circumference is 24,901 miles and a day is 24 hours, Earth rotates at about 1000 miles per hour. In general, Earth shape is an oblate spheroid flattened at the poles.
Because earthquakes can rearrange Earth’s mass, they can speed up, slow down, or have no effect on Earth’s rotation. For example, figure skaters spinning with their arms to move faster. But when they put out their arms, they spin more slowly.
“Back in the 1940s, researchers found that the Earth speeds up and slows down a bit as it spins. Because of this, we use atomic clocks that measure time precisely.”
How does rotation impact living things?
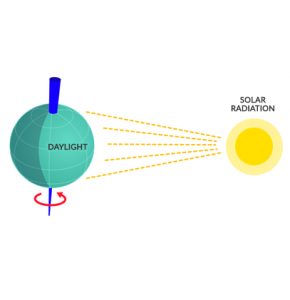
Because the Earth rotates, it’s more than physics that makes this phenomenon interesting.
- It’s not only physics but Earth’s rotation affects us biologically. For example, our bodies are programmed to sleep based on Earth’s rotation.
- The Earth is slowing down because the moon’s pull affects its rotation. But it’s very negligible with little effect.
- While half the Earth is in sunlight, the other half is in darkness. This is similar to the phases of the moon.
Who tracks and measures Earth’s rotation?
International Earth Rotation and Reference System Service (IERS) is the authority group that measures Earth’s rotation. But it’s not only that.
Does the Earth wobble on its axis? How long are days? Are there plate tectonic movements? They measure these types of phenomena too!
In addition, IERS produces the International Terrestrial Referencing System (ITRS). This reference system gives a set of coordinates for points on Earth’s surface. But it includes the motion of Earth’s crust so you can compare two points in time.
Do you have any more interesting facts about the day-night boundary? Please let me know with a comment below.
Resources
Globe Day-Night Viewer
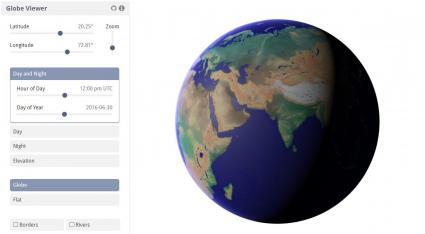
The Globe Viewer shows the day-night boundary in real-time which depicts the exact division between the illuminated day side and the darkened night side of the planet.
This boundary, also known as the terminator, constantly shifts as the Earth rotates on its axis, allowing users to observe the transition between day and night across different regions. If it’s nighttime in your hometown, check and see if it’s not being lit up by the sun.
Earth Rotation: The Day-Night Boundary
Earth’s rotation is a cycle of 24 hours. But the Earth actually turns once every 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds.
This period is known as a sidereal day and is the time it takes for a specific point on the Earth’s surface to return to the same position relative to the distant stars.
The reason for this discrepancy between the sidereal day and the 24-hour day we use in our daily lives.
If you have any questions or comments about Earth’s rotation, please feel free to contact us below.







You don’t complete your sentence :
“The reason for this discrepancy between the sidereal day and the 24-hour day we use in our daily lives.” . . . . . is …….
When is it Saturday and Sunday at the same time on earth. Is there a side real segment in time where the 2 days overlap?
What do you need to know?
I’m in need of more information, thanks
If a day on earth is 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds, does that mean that all of the time that is missing from each day is added up and is transformed into another day every four years AKA a leap year?
I believe you are referring to “leap years” when you add a day to the calendar year every 4 years. It usually gets added on February 29
How do they make up the time in the 24 hour time cycle ?
( 4 minutes)
At 03:00:00 UTC time, it’s dark in both Mexico and Jerusalem. But I guess it would be close to morning for Jerusalem at that time.
Here’s a map for visual. https://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/sunearth.html?iso=20181207T0220
Can there be night time in Mexico City and also at the same time be night in Jerusalem?