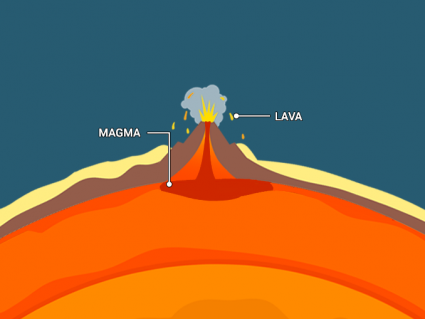
Characteristics of Soils
Introduction to Soil
Soil is a key part of our planet. They have many characteristics, each with unique features. In this blog post, we’ll explore different soil characteristics.
We’ll see how these traits affect plant growth and the environment. Understanding these characteristics of soils can help you with farming, gardening, and any project with soil.
Chalky Soil

We can recognize chalky soil by its light color. This is because of its alkaline nature and it has a high pH. Although it struggles to retain water and nutrients, it’s not entirely infertile.
Plants in this soil often face challenges because it’s mostly calcium carbonate from built-up sediment. But with proper management, it’s possible to mitigate these issues.
While challenging, chalky soil offers unique gardening opportunities. If you carefully select suitable plants and soil improvements, you can turn it into a thriving garden.
Saline Soil

We can recognize saline soil for its high salt content. The high salt levels can hinder their water absorption, making it detrimental to most plants.
This saltiness often comes from evaporating water in dry climates. It can also result from poor drainage or sea spray in coastal areas.
Despite these challenges, some specialized crops and plants have adapted to thrive in saline soils. This includes salt-tolerant plants like mangroves, sea lavender, and certain types of barley and wheat.
Sulfuric Soil

Sulfuric soils are unique and less common. They form in wet, oxygen-poor environments such as areas with volcanic activity.
When exposed to air, these soils become highly acidic. This high acidity can harm the growth of vegetation so it’s not ideal for agricultural production.
But believe it or not, some bacteria and plants have adapted to survive in sulfuric soils. For example, certain types of grasses and sedges can tolerate the high acidity of sulfuric soils.
Laterite Soil

Laterite soil is a type of tropical soil that forms in hot and wet climates. It is rich in iron and aluminum so it has a red or brown color to it.
This type of soil tends to be acidic and nutrient-poor, which can be challenging for conventional agriculture. Despite these limitations, laterite soil isn’t barren.
For example, plants like tea, coffee, and cashew nuts can grow well in laterite soil. While laterite soil limits some agricultural practices, it uniquely benefits specific crops.
Characteristics of Soils
From chalky to laterite, each type of soil presents unique challenges and opportunities. By choosing the right plants for each soil type, we can cultivate thriving ecosystems.
Do you have any questions about the characteristics of soils? Please let us know in the comment section below.