How Volcanoes Form Igneous Rocks

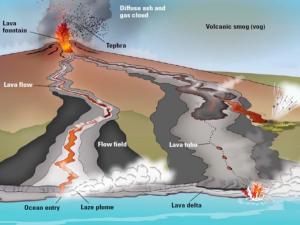
Volcanoes are the foundation for igneous rocks. When volcanoes erupt, hot lava drips on the side of volcanoes then cools and hardens. This becomes igneous rocks like granite.
Igneous rocks can also form deep inside the Earth from magma. So, without igneous rocks, there wouldn’t be the rock cycle.
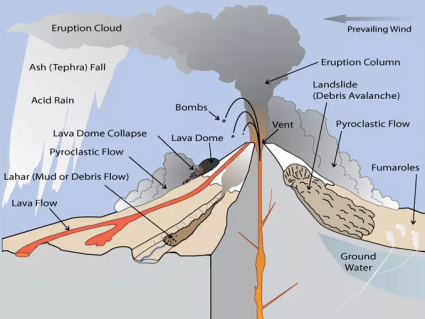
“Like a bottle of champagne with a cork in it, liquid rock pools in the magma chamber. Like pulling a cork, the volcano erupts from immense pressure. Down the mouth of the volcano, lava spews forming igneous rocks.”
How do igneous rocks form?
Igneous rocks form after cooling and solidifying from magma or lava. So when molten rock cools, they turn into solid material and become igneous rocks. First, you have to understand the difference between lava and magma. And it’s all about location.
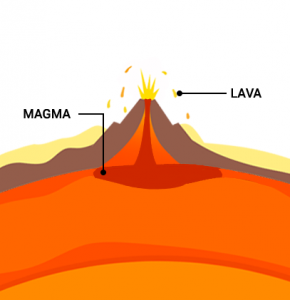
For a volcano when it’s deep inside the Earth, it’s magma. Once it erupts, it’s lava. Then, it cools and solidifies. But it matters where it cools and solidifies.
Because of the immense pressure that igneous rocks undergo, it erases any fossil evidence. Likewise, this is true for the immense heat from metamorphic rocks. So if you see a rock with a fossil, you can automatically assume that it is a sedimentary rock.

Obsidian, rhyolite, basalt, and scoria are members of the igneous rock family. These types of rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. They all vary in cooling rates and chemical compositions leading to different types.
What are the two types of igneous rocks?
There are two types of igneous rocks. Based on texture and composition, we can classify them into two categories:
- INTRUSIVE: Intrusive (or plutonic) rocks form inside the Earth from magma.
- EXTRUSIVE: Extrusive rocks cool and solidify on the surface.
For intrusive (or plutonic) rocks, magma is hot inside the Earth so it cools slowly. When it cools, minerals form slowly. So crystals grow very large for intrusive igneous rocks. For example, gabbro, granite, and pegmatite are intrusive rocks.
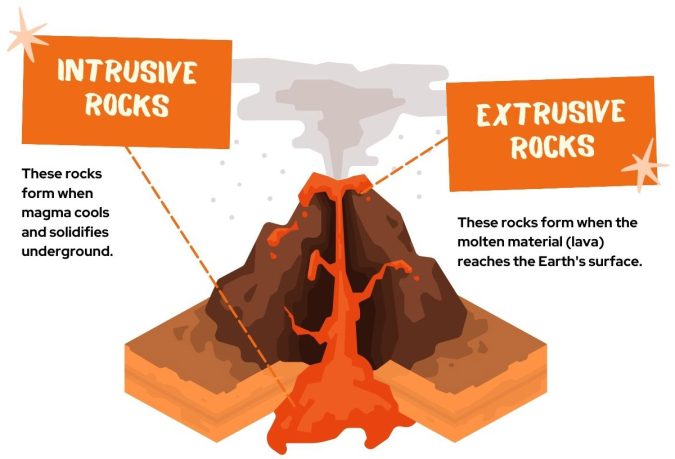
For extrusive rocks, because they cool quickly, the crystals are smaller. Some types of extrusive igneous rocks can even have pockets of air bubbles inside them. For example, extrusive rocks include basalt, andesite, and obsidian.
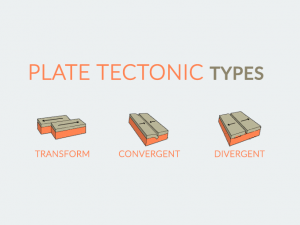
The Relationship with Plate Tectonics
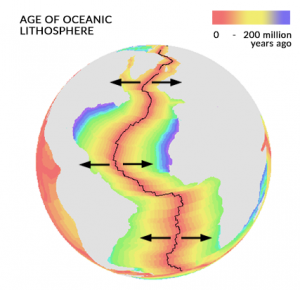
Hidden beneath Earth’s oceans, underwater volcanoes spew out lava at mid-oceanic ridges (rift valleys). Because divergent plates move apart from each other at these mid-oceanic ridges, magma flows upwards from the mantle beneath.
When the lava hardens, it becomes dark, dense igneous rock known as “basalt” at rift volcanoes, contributing to the Earth’s diverse geology.
Because divergent plates fill in the gaps with basalt, the oceanic crust turns out to be very young geologically. Over time, the plates grow at the oceanic crust, and older rock is pushed away from mid-oceanic ridges.
How Volcanoes Form Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are the rocks that form when lava cools and solidifies. It’s important for volcanologists and geologists to study the different types of igneous rocks because they can tell us a lot about how volcanoes work and what conditions they are in generally.
Get back to us with a question or comment by using the comment form below about igneous rocks.







I loved learning it so much.
It taught me a lot
Awesome!!!
I like this passage because it talks about how rocks come out the volcanoes and are called “igneous rocks”.