What Is the Mesosphere?
Highlights of the mesosphere
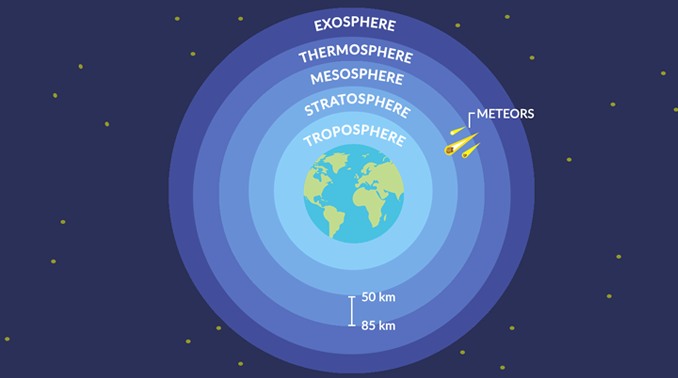
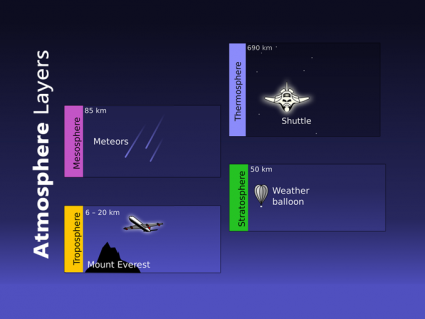
The mesosphere is the third layer of the atmosphere. It spans a vertical distance from 50 to 90 km.
Here are some of the highlights of the mesosphere:
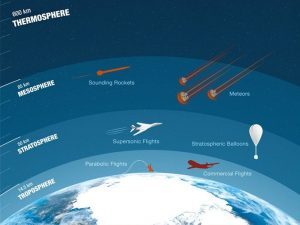
Where is the mesosphere?
This image shows where the mesosphere is located in the atmosphere.
The thermosphere which consists of the ionosphere and exosphere is above the mesosphere. These layers of the atmosphere contain just 0.001% of the air mass over the Earth.
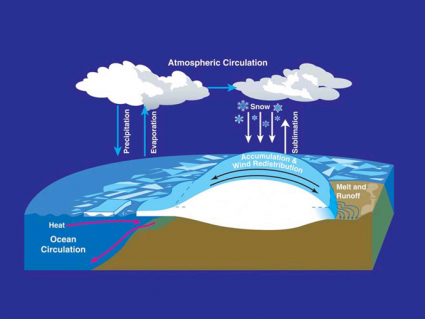
“The mesosphere spans a vertical distance between 50 to 90 km. It’s sandwiched between the stratosphere below and the thermosphere above”
The mesosphere breaks up meteors
If space rocks fall towards Earth, it’s in the mesosphere where they burn up. But if any space rocks get through the mesosphere, the ones that hit Earth are called meteorites.
The mesosphere layer protects the Earth from large meteoroids. It’s in the mesosphere where it serves as a shield for meteorites.
Friction in the mesosphere burns up meteors. Then, they disintegrate into small pieces of dust. From our eyes, we see the ionized trails left by the remains of meteors.
What is the air temperature in the mesosphere?
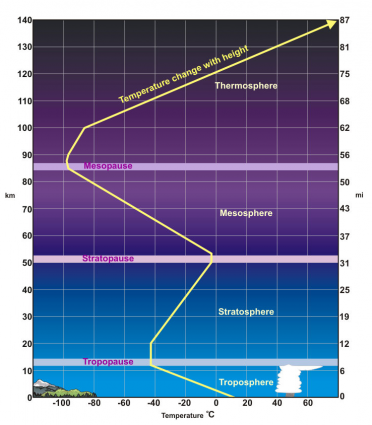
Temperature decreases with height in the mesosphere. In fact, temperatures can reach as low as 100 K in this layer of the atmosphere.
Remember that the ozone layer in the stratosphere below absorbs ultraviolet radiation and elevates temperatures. This is why it’s an inverted temperature gradient upward to the stratopause.
Then, the mesopause is the altitude at which the temperature reaches a minimum before increasing with height in the thermosphere.
What Is the Mesosphere?
The mesosphere is the second major layer of Earth’s atmosphere, from about 50 to 85 kilometers (30 to 55 miles) above the surface. It sits directly above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere.
It is characterized by extremely low air pressure and temperatures that can drop as low as -90 degrees Celsius (-130 degrees Fahrenheit), making it a region where meteors burn up upon entry due to the sparse air molecules.
Do you have any questions about the atmosphere and how it relates to the mesosphere? Please let us know with a comment below.







In mesosphere temperature decreases with height
Really love the explanation. Everything is accurate.