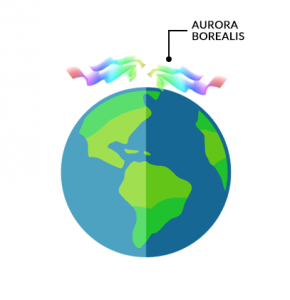
Aurora Borealis Facts: How the Northern Lights Work

“Named after the Roman goddess “Aurora”, the Aurora Borealis is a light spectacle that occurs naturally from electrically charged particles in the magnetosphere.”
The colors vary from green, yellow, purple, and red that stream in the upper region of the atmosphere.
We can observe the Northern Lights because solar winds eject electrically charged particles directed to Earth.
The solar winds interact with Earth’s magnetosphere which triggers the dazzling display of the Aurora Borealis.
But more on that later. Let’s talk about Earth’s magnetic field first.
How do solar winds disturb the magnetosphere?
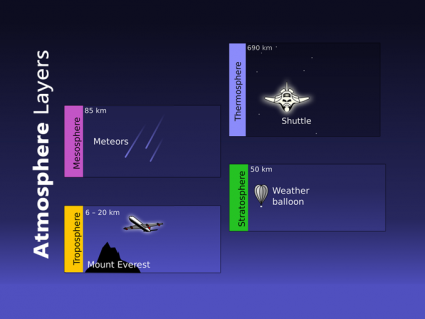
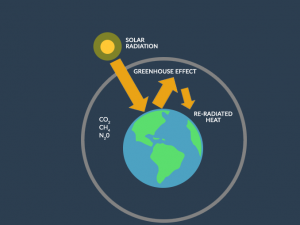
The magnetic field gives us a layer out in space called the magnetosphere. It varies in distance but can extend up to 65,000 kilometers from Earth’s surface.
From space, the magnetosphere resembles a magnetic dipole. Field lines resonate in a circular pattern. Instead of the geographic north and south poles, they resonate from the magnetic poles.
The magnetosphere allows life to exist on Earth’s surface. Without it, Earth would be exposed to cosmic and solar radiation from the sun.
“Contributing makes me feel like I’m being useful to the planet. During magnetic storms, trapped plasma flashes lights that are observable around the globe. This disturbance in the magnetosphere is what creates the Aurora Borealis.”
Why do solar winds travel down field lines?
As the sun emits solar winds, it sends lots of other energy and small particles our way.
- SOLAR WINDS: When these solar winds reach Earth, they hit our protective layer called the magnetosphere.
- FIELD LINES: But the waves don’t just collide into the surface. They hit the magnetosphere. The waves travel down the magnetic field lines in Earth’s atmosphere. These field lines converge at the magnetic poles which is why the Aurora Borealis glows most remarkably there.
- LIGHT DISPLAY: This is where it interacts with oxygen, nitrogen and other elements with a dazzling display of lights in the sky.
Why do the aurora borealis have different shapes and colors?

As we have learned, charged particles mingle with gases to generate the beautiful northern lights. But why do these charged particles vary in color?
It mainly depends on the gases that are present in the atmosphere. For example, oxygen emits green and red light. But nitrogen glows blue and purple.
The shape depends on a variety of factors. From space, the aurora borealis looks like a ring around the magnetic pole. It generates other shapes depending on where in the magnetosphere the electrons arrive from.
Is there Aurora Borealis on other planets?
The Aurora Borealis isn’t unique to Earth. Other planets in the solar system have similar displays of light.
- JUPITER: For example, solar storms cause huge auroras on Jupiter. In fact, it glows much brighter than Earth because its tremendous size gives it more electrical potential.
- SATURN: Saturn’s aurora is only visible in ultraviolet light. This means that it requires special instruments to view it.
- MARS: Mars has an even more bizarre type of aurora. Scientists have found it to glow only on the one side of the planet that has sunlight.
Auroras are the most beautiful things in the sky. They can be seen from specific areas of the world, and they have a great deal to tell us about our planet.