What Is the Stratosphere?
DEFINITION:
The stratosphere is the second layer of Earth’s atmosphere, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. It starts about 12 to 15 km (6 to 9 miles) above Earth’s surface and goes up to about 50 km (31 miles) and contains the ozone layer.
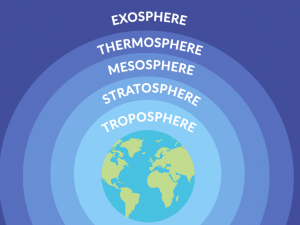
The Stratosphere
The stratosphere extends from about 12 to 50 km upwards. It’s sandwiched between the troposphere below and the mesosphere above.
The major highlights of the stratosphere include:
Here are more details on the stratosphere and its influences on Earth.
Where is the stratosphere in the atmosphere?
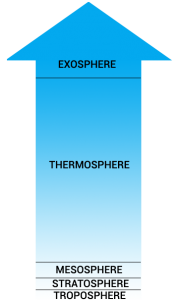
The stratosphere is the second atmospheric layer from the ground level. It sits above the troposphere and is directly below the mesosphere.
The stratosphere is bounded by the tropopause and stratopause. It’s characterized by a highly stable temperature gradient that cools from top to bottom.
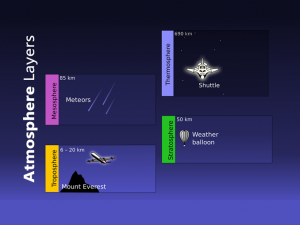
Although variations in altitude exist, it’s roughly between 12 to 50 km above sea level. Specifically, the geography and time of season influence the lower bound.
For example, the tropics have an average troposphere height of 18 km. But the polar regions have a troposphere upper bound altitude of about 6 km.
Is ozone concentrated in the stratosphere?
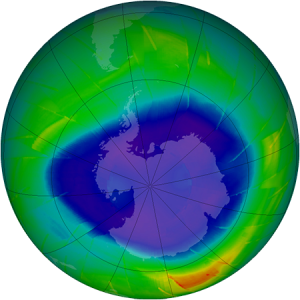
The stratosphere is filled with ozone gas, which is the three-atom form of oxygen. And ozone is concentrated at about 25 km. It’s in the stratosphere where O2 may be photolyzed by solar ultraviolet radiation to form the ozone layer.
Any high-frequency radiation such as x-rays, ultraviolet, and gamma rays are harmful to living tissues. This can cause cells to become cancerous.
This protective layer is essential for life because it absorbs ultraviolet radiation. Without ozone in the stratosphere, ultraviolet light from the sun would damage all living things on the planet.
What is air temperature like in the stratosphere?
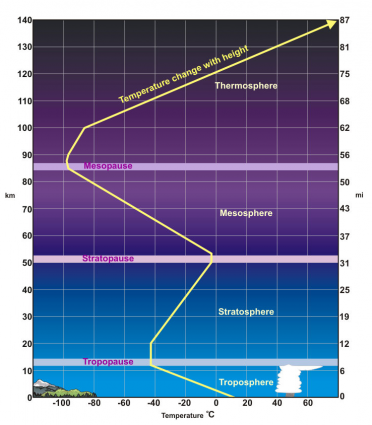
Ozone is the main reason why temperature increases in the stratosphere. It’s at this 25 km concentrated ozone mark where ultraviolet radiation is absorbed.
Consequently, the absorbed light causes air temperature to rise. This is why as you move upwards in the stratosphere, air temperature increases.
Then, air temperature continues to rise until it hits the mesopause. Finally, maximum heating occurs when it reaches the top part of the stratosphere.
The environmental lapse rate (ELR) measures how much temperature decreases with height. But because air temperature increases up to the stratopause, the lapse rate is negative in the stratosphere.
Does water vapor exist in the stratosphere?
If you look at water vapor, 99% is found in the troposphere. This is why most weather takes place here.
Weather patterns dump rain moving water vapor through the troposphere. Consequently, this moisture availability influences floral and fauna in various environments.
But water vapor can scarcely survive by vertically moving into the stratosphere. Clouds initially form in the troposphere. But tall cumulonimbus can ascend through the tropopause reaching far into the stratosphere.
What Is the Stratosphere?
The stratosphere is the second major layer of Earth’s atmosphere, located above the troposphere and extending from about 12 kilometers (6 miles) to approximately 50 kilometers (31 miles) in altitude.
It is characterized by a stable temperature profile, with temperatures increasing with altitude due to the presence of the ozone layer, which absorbs and scatters ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun, serving as a protective shield for life on Earth.
If you have any questions about the stratosphere, please let us know with a comment below.






This really helped me get my assignment done in time😊! A real lifesaver.
Great study material! This website’s a life saver.😊
I have a project due tomorrow and that really helped me grasp the concept of what I need to work on. BTW, I have college exams soon, please pray for me.😬
Really helpful. Thanks!
Really helped. Thanks!
Where are the other layers for the pic 🤨
I would like to use your image of Earth’s atmosphere in my book. The book is titled
“Earth 10,000 Years With Man. I am requesting that you grant me permission to use your image in my book.
Very resourceful. 🙂 Thanks
Very helpful. Thanks.
WOW,an eye-opener, and very educational. I would like to learn more