Human Evolution: A Timeline of Early Hominids [Infographic]
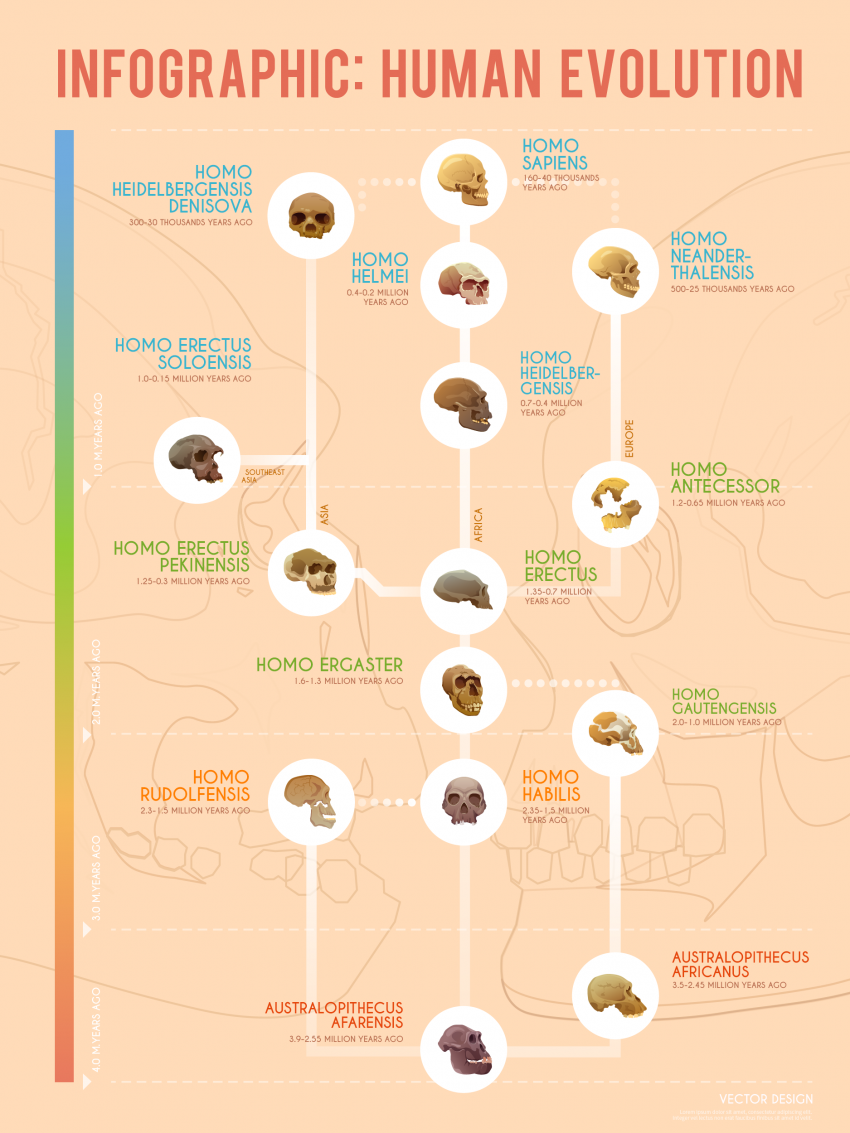
“For about 4 million years, human evolution has been a long, long process. From the early hominids to modern humans, we are in the process of evolving at this very moment.”
Mammals existed during the era of dinosaurs. But they kept a low profile and remained small and fury like a hamster.
After the extinction of the dinosaurs, this marked the Age of Mammals. Because dinosaurs went extinct, mammals emerged as the largest land animals at this time.
Hominids were the early proto-humans. They were known for sharpening objects with silicon rocks. They began to master the use of their hands and fingers.
Let’s explore these early hominids (proto-humans), each species, and where they evolved geographically.
1. Australopithecus Afarensis
Australopithecus Afarensis was the earliest form of hominids, which archaeologists dug up fossils in the Afar Triangle of Africa, hence the name “Afarensis”.

- Australopithecus afarensis is an extinct hominin species that lived approximately 3.9 to 2.9 million years ago during the Pliocene and early Pleistocene epochs.
- They are believed to be among the earliest hominins, with a mixture of ape-like and human-like features.
- The most famous individual of this species is “Lucy,” a nearly complete skeleton discovered in Ethiopia in 1974.
- Australopithecus afarensis had a small brain relative to modern humans, indicating limited cognitive abilities.
- They were bipedal, walking on two legs, which is a significant adaptation in hominin evolution.
- The species likely lived in wooded environments and had a diverse diet, including both plant and animal-based foods.
- Australopithecus afarensis individuals were relatively small in stature, with males and females exhibiting sexual dimorphism in body size.
- Fossil evidence suggests they used tools, but their tool-making capabilities were limited compared to later hominin species.
2. Australopithecus Africanus
Australopithecus Africanus is the first of the early ape species classified as hominids.

- Australopithecus africanus is an extinct hominin species that lived between 3.5 and 2.4 million years ago in Southern Africa during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs.
- It is known for being one of the first hominins to be discovered and described from Africa.
- Australopithecus africanus had a combination of ape-like and human-like features, such as a small brain size relative to modern humans and a bipedal upright posture.
- These hominins likely lived in woodlands and grasslands, which influenced their diet, consisting of both plant and animal foods.
- Although they were not advanced tool users, they may have used simple tools, such as rocks and sticks, for various purposes.
- Australopithecus africanus individuals had a facial structure that resembled apes more closely than modern humans, with a projecting face and pronounced brow ridges.
3. Homo Hablis
About 2.35 – 1.5 million years ago, Homo Habilis had larger brains which helped their survival.

- Homo habilis, which means “handy man,” is an extinct species of early humans that lived approximately 2.4 to 1.4 million years ago during the early Pleistocene epoch.
- They were among the first members of the Homo genus and are considered one of our direct ancestors.
- Homo habilis exhibited significant advancements compared to earlier hominins, including the use of tools, which is reflected in their nickname.
- The Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania is a significant archaeological site where many Homo habilis fossils and stone tools have been discovered.
- Their brain size was larger than that of earlier hominins but still smaller than modern humans, suggesting some cognitive development.
- Homo habilis had a more upright posture and a bipedal gait, allowing them to walk on two legs efficiently.
- Their diet likely consisted of a variety of foods, including plant materials and scavenged or hunted animals.
- The species played a crucial role in the transition from australopithecines to more advanced Homo species like Homo erectus.
- While they primarily used simple stone tools, their ability to fashion and use tools marked a significant milestone in human evolution.
4. Homo Rudolfensis
Homo Rudolfensis is an extinct hominin species that lived during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs, around 2.4 million years ago.

- This species is known from fossil remains discovered near Lake Turkana in Kenya, specifically at Koobi Fora.
- The exact classification of Homo Rudolfensis is debated, and some researchers consider it a distinct species, while others propose it may be a variation of Homo habilis.
- Fossil evidence of Homo Rudolfensis includes a relatively large and rounded braincase, indicating a larger brain size compared to earlier hominins.
- They exhibited a more human-like facial structure and dental characteristics, but the overall body size and limb proportions were still primitive.
- Homo Rudolfensis is associated with the use of simple stone tools, suggesting some level of toolmaking and tool use.
5. Homo Gautengensis
Homo Gautengensis is a proposed hominin species that is not widely accepted by the scientific community.

- It is hypothesized Homo Gautengensis to have lived around 2 million years ago in South Africa.
- Fossil evidence for this species is sparse and contentious, making it difficult to establish its place in human evolutionary history.
- Some researchers suggest that Homo Gautengensis may represent a regional variation or a subgroup within the broader category of early Homo.
- Like other early Homo species, it likely had a relatively small brain size compared to modern humans but exhibited some adaptations associated with bipedalism.
- Homo Gautengensis had big teeth for chewing plants, consumed more vegetables, and likely had smaller brains.
- They also may have used fire and stone tools.
6. Homo Ergaster
Homo Ergaster is an extinct hominin species that lived approximately 1.6 to 1.3 million years ago during the early Pleistocene epoch.

- The nickname for Homo Ergaster is “Workingman” because they built more sophisticated stone tools (archaeologists often discovered hand-axes and cleavers near skeletons found).
- Fossil evidence for Homo Ergaster is primarily associated with sites in Africa, such as Koobi Fora in Kenya and Dmanisi in Georgia.
- They are considered one of the early members of the Homo genus and represent an important transitional species between earlier hominins like Homo habilis and later ones like Homo erectus.
- Homo Ergaster is known for its more modern and human-like characteristics, including a relatively larger brain size and a more developed body structure for endurance running.
- They exhibited a pronounced reduction in facial prognathism (forward projection of the face) compared to earlier hominins.
- Homo Ergaster is associated with the Acheulean stone tool industry, characterized by the creation of bifacial handaxes and cleavers.
- Their hunting and scavenging abilities, along with the use of fire, likely played a crucial role in their survival and expansion.
7. Homo Erectus
Homo Erectus lived approximately 1.3 million to 0.7 years ago and was found along the southern coast of Asia.

- They are considered one of the first hominin species to have expanded out of Africa and colonized different parts of the world.
- Fossil evidence for Homo Erectus has been found in various locations, including Africa, Asia, and Indonesia.
- Homo Erectus is characterized by a more modern and human-like anatomy compared to earlier hominins. They had a larger brain size because they were believed to eat more meat.
- They are believed to have been the first hominin species to use fire deliberately, which had significant implications for cooking, warmth, and protection.
- Homo Erectus is considered a crucial transitional species in human evolution, bridging the gap between earlier hominins and anatomically modern humans.
- Their migration out of Africa is a significant milestone in human prehistory, leading to the colonization of different regions and adaptation to diverse environments.
8. Homo Erectus Pekinesis

Homo Erectus Pekinesis existed 1.25 – 0.3 million years ago and their fossils were mostly found near Beijing (Peking).
- Homo Erectus Pekinensis is a subspecies of Homo erectus and is best known for the discovery of fossils in Zhoukoudian (Choukoutien), near Beijing, China.
- Fossils of Peking Man were discovered in the 1920s and 1930s and played a significant role in our understanding of human evolution.
- They are associated with the use of tools and evidence of fire use, suggesting advanced cognitive and cultural abilities.
- They are known as “Peking Man” because these fossils were mostly found near Beijing (Peking).
- These extinct hominids were known to have heavy brow ridges and the use of stone tools.
- The study of Peking Man contributed to our understanding of hominin dispersal and adaptation to different environments, particularly in East Asia.
9. Homo Antecessor
Homo Antecessor is recognized as “Human Pioneer” due to the belief they belonged to the first human population in Europe.

- Homo Antecessor is an extinct hominin species that lived during the Lower Pleistocene epoch, approximately 1.2 million to 650,000 years ago.
- Fossil evidence for Homo Antecessor was discovered at the Gran Dolina site in Atapuerca, Spain, and at other locations in Europe.
- The name “antecessor” means “pioneer” or “ancestor” in Latin, reflecting its position as a possible common ancestor to both Neanderthals and modern humans.
- This species is characterized by a combination of primitive and more advanced features. It had a relatively small brain size but showed evidence of tool use and possibly meat consumption.
- The discovery of cut marks on animal bones at the Atapuerca site suggests that Homo Antecessor was involved in butchery and hunting activities.
- Some researchers suggest that Homo Antecessor may have been one of the first hominins to inhabit Europe, making it an important part of the continent’s prehistory.
10. Homo Erectus Soloensis
About 1.0 – 0.15 million years ago, scientists discovered this type of hominid in Indonesia on the island of Java.

- Homo Erectus Soloensis is a subspecies of Homo Erectus known from fossil remains found in the Solo River region of Java, Indonesia.
- These fossils were discovered in the 1930s and are sometimes referred to as “Solo Man” or “Ngandong Man” after the nearby Ngandong village.
- Homo erectus soloensis is estimated to have lived around 150,000 to 1,000,000 years ago during the Middle and Late Pleistocene.
- The fossils include skullcaps, teeth, and other skeletal elements, providing insights into the anatomy of this subspecies.
- Like other Homo erectus populations, Homo erectus soloensis is characterized by a relatively large brain size compared to earlier hominins.
- They are associated with the use of Acheulean stone tools, which are more advanced than the tools used by earlier hominins.
- Evidence of fire use has also been found at some sites, suggesting an ability to control and control fire.
11. Homo Heidelbergensis
About 0.7-0.4 million years ago, Homo Heidelbergensis existed in both Africa and Europe. But archaeologists found fossils of Homo Heidelbergensis near Heidelberg Germany (hence the name).

- Homo Heidelbergensis is an extinct hominin species that lived during the Middle Pleistocene period, approximately 700,000 to 400,000 years ago.
- Fossil evidence for Homo heidelbergensis has been found at various sites across Africa, Europe, and possibly Asia, indicating a wide geographic distribution.
- This species exhibits a mix of primitive and more advanced anatomical features. They had a larger brain size compared to earlier hominins, suggesting increased cognitive abilities.
- Homo Heidelbergensis is associated with the development of more sophisticated stone tools, including handaxes and cleavers, which are characteristic of the Acheulean industry.
- Some researchers believe they are most notable for possibly burying their dead.
- They were likely skilled hunters and gatherers, capable of using fire and building simple shelters.
- The species demonstrates adaptations to various environments, from temperate regions in Europe to more tropical climates in Africa.
12. Homo Helmei
There is uncertainty about Homo Helmei compared to other hominin species. About 0.4 – 0.2 million years ago, Homo Helmei existed only for a short period of time.

- Homo Helmei is theorized to have displayed a unique combination of physical traits, blending features from different known hominin species.
- Although they are a speculative hominin species, researchers propose they are known for their out-of-Africa movement and that their brain volume is slightly larger than modern humans.
- Research is still being developed to improve our understanding of Homo Helmei.
13. Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Neanderthalensis, or Neanderthals, is an extinct species of hominins closely related to modern humans (Homo sapiens).

- Neanderthals lived in Eurasia and Africa from approximately 500,000 to 25,000 years ago.
- They had a robust build with stocky bodies, adapted for cold climates.
- Prominent features included a large brow ridge, strong jaw, and a wide nose.
- Evidence suggests they had the ability to speak and may have used complex language.
- Neanderthals were skilled hunters and gatherers, using tools such as spears and handaxes.
- They lived in small, close-knit groups and had social structures.
- Evidence of burial practices suggests a degree of ritual and symbolic behavior.
- Studies have shown that some modern humans of non-African descent carry small percentages of Neanderthal DNA, indicating limited interbreeding between the two species.
14. Homo Sapiens
About 160-40 thousand years ago, the “doubly wise man” was the recent form of modern humans “homo sapiens sapiens”.

- Homo sapiens is the only surviving species in the Homo genus and the only extant hominin species.
- Homo sapiens were known for their artistic talents in cave paintings and clay work.
- They made hooks and spears to catch fish and invented the spear thrower. Thus, it made them better hunters because they could hunt from a distance.
- They have a high forehead, less prominent brow ridges, a rounded skull, and a vertical face. Modern humans have a complex vocal apparatus that allows for advanced language and communication.
- Homo sapiens coexisted with other hominin species, including Neanderthals and Denisovans, for some time.
Homo sapiens is the only surviving hominin species, and their success is attributed to their unique combination of cognitive abilities, culture, and adaptability, which allowed them to thrive and become the dominant species on Earth.
A Timeline of Human Evolution
Since about 4 million years ago, humans have evolved from early hominids to modern humans. Here are 14 species examples from human evolution now extinct.
Apes remained in trees as their primary food source. Eventually, grass began to spread in places like the African Savannah. Because there were fewer trees, this forced apes to walk to new food sources.
With their heads above the grass to see predators, apes evolved by walking on two legs. It also helped to have their hands available when they were traveling. So here we are at this point in human evolution.
Do you have any general questions about the theory of evolution? Please send us your comments and questions below.



Here’s information on how to cite – https://earthhow.com/how-to-cite
nice resource but how can I cite this
How did the human nose evolve?
The chart & the timeline is magnificent! It makes me from:[Oh~, do we have to read it?] to [WOW! Can I read it again & again?]. You should make more & more~!
This is a common misunderstanding of evolutionary theory. Humans did not evolve from any of the modern apes (like chimpanzees, gorillas, or orangutans) we see today. Instead, humans and the modern apes share a common ancestor that lived millions of years ago. This ancestor was neither a human nor a modern ape… but a different species from which both have evolved along separate evolutionary paths.
Please see our article on the Theory of Evolution – https://earthhow.com/theory-of-evolution/
If we evolved from apes why are there apes still living to this day.
Thank you
Very well done, and refreshingly simple, so I will recommend it,
And come back;”-))
My DNA goes back to Africa 200,000 years ago when ancestors left Africa. I am also .003% Neanderthal. Do you have anything about my ancestors at that tie in Europe?
Great timeline, did this for history project and yes, you did miss some groups.
Do we know yet where Australopithecus anamensis fits into the picture?
Hi, love the chart you made. Wanted to share these with you as I didn’t see listed in case you were interested in including them. The Homo Naledi and the Home Floresiensis. Links with a bit more info are below.
https://news.nationalgeographic.com/2017/05/homo-naledi-human-evolution-science/
http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-fossils/species/homo-floresiensis