Endosymbiosis: The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells
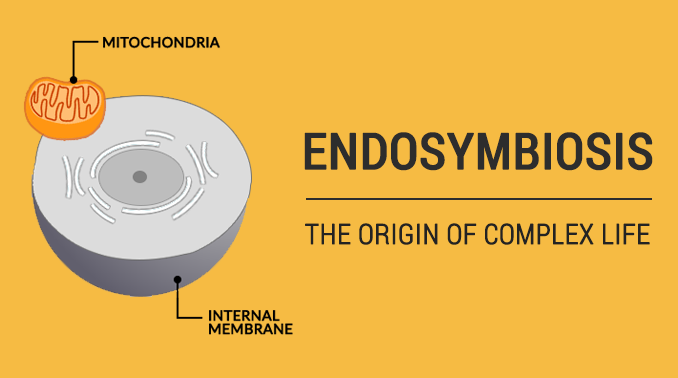
What is Endosymbiosis?
Endosymbiosis is the process that sparked the origin of eukaryotic cells on Earth.
It’s the idea that a prokaryote engulfed a bacteria capable of aerobic respiration.
Then, this turned into mitochondria and became part of a eukaryotic cell.
Because they both symbiotically gain from the encounter, they asexually multiply and evolve this way.
Evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes
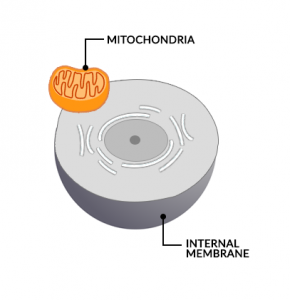
Long ago, mitochondria were living organisms all by themselves. It lived freely doing aerobic respiration.
The idea of endosymbiosis starts with a mitochondrion latching onto a prokaryote. Next, the prokaryote engulfs it as part of its cytoplasm.
So the mitochondrion leverages the nutrient-rich surrounding of the prokaryote. And in return, the prokaryote receives energy from the mitochondria powerhouse during its permanent residence.
“The mitochondria once lived free but are now part of complex cells. So the eukaryotic cells originated from endosymbiosis.”
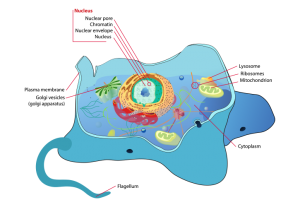
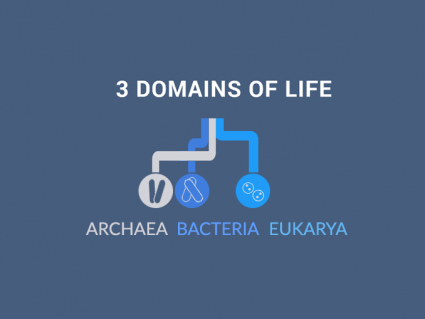
Eukarya have a nucleus
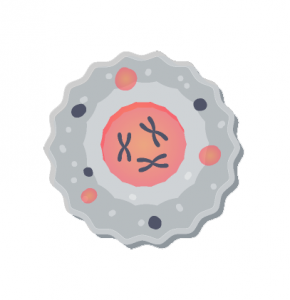
One of the key differences between eukaryotic cells is that they have organs that are sealed off from the rest of the environment.
They have a nucleus that houses chromosomes and DNA. Further to this, eukarya have organelle like mitochondria (through endosymbiosis) and chloroplasts all within their cell membrane.
Even though single-cell eukarya exist, eukaryotes are mostly multicellular. For example, the plant and animal kingdoms are mostly multicellular.
Endosymbiosis: The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells
An endosymbiotic theory states that the eukaryotic cells and mitochondria originated from a single-celled organism, which eventually became two separate cells.
This theory has had a profound impact on our understanding of the evolution of complex life forms and the symbiotic relationships that shaped the development of eukaryotic cells.
Do you have any questions? Please send us a comment below to get a better understanding of endosymbiosis and the biology of us.



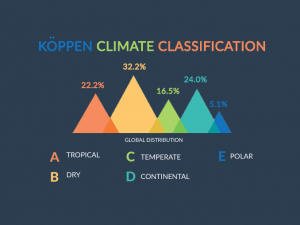
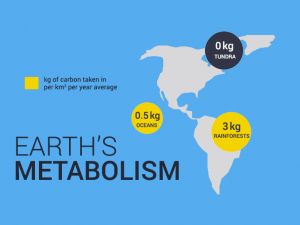
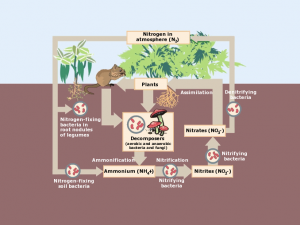
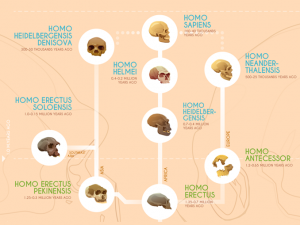
“An endosymbiotic theory states that the eukaryotic cells and mitochondria originated from a single-celled organism, which eventually became two separate cells.”
This statement is completely confused; it makes no sense. Additionally the diagram of endosymbiosis shows a nucleus with only one membrane and the plasma membrane labelled as “internal membrane”. You seem to have no idea what you are talking about.
You claim that “Even though single cell eukarya exist, eukaryotes are mostly multicellular”. This is an incorrect statement since there are way much more single cell protists.