What Are the 3 Domains of Life?
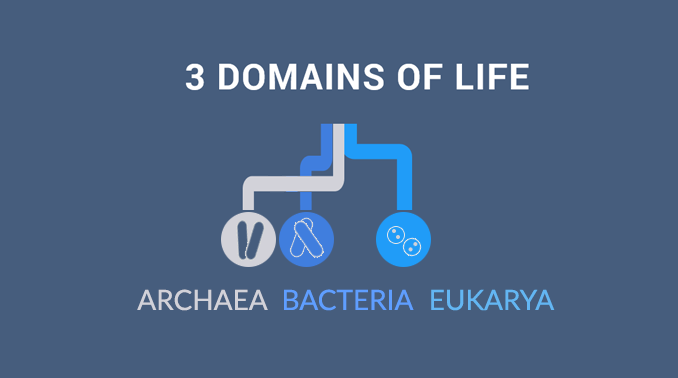
The 3 Domains of Life
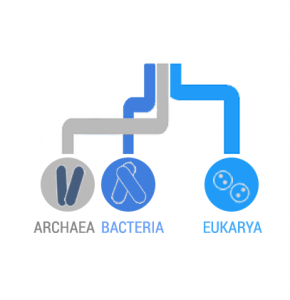
All living organisms can be categorized into 3 domains of life:
- Eukaryotes
- Prokaryotes
- Archaea
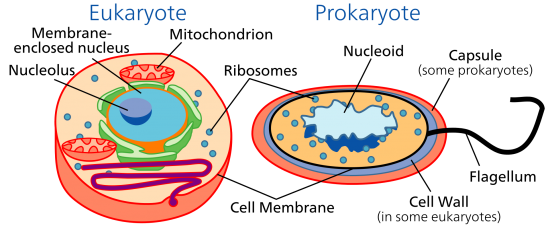
DOMAINS: “Domains” are the top-level classification that categorizes life in the most general way. For example, it separates the presence of a nucleus. Prokaryotes like archaea and bacteria don’t have one. But eukarya have a nucleus.
But there’s a bit more to it than that. Here are more differences between the 3 domains of life.
1. Eukaryotes
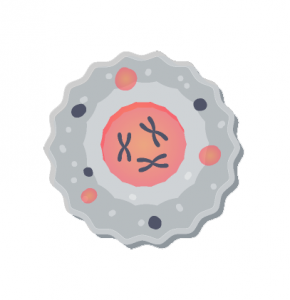
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that houses chromosomes and DNA. Furthermore, eukarya have organelle like mitochondria and chloroplasts all within a cell membrane.
Even though single-cell eukarya exist, eukaryotes are mostly multicellular. For example, the plant and animal kingdoms are mostly multicellular. On the other hand, the protozoa, fungi, and algae kingdoms have unicellular eukarya.
Eukarya are resistant to traditional antibiotics. And finally, eukarya allay doesn’t have peptidoglycan which exists in bacteria. This protects their envelope and maintains its shape.
2. Prokaryotes
Bacteria don’t have any cell organelles and are without a nucleus (prokaryotes). If you break down the word prokaryote, “pro” means “before” and “karyote” means “nucleus”. So by definition, prokaryotes have existed long before the evolution of a nucleus (such as those found in eukarya).
Bacteria cover a large group of unicellular microorganisms. These single-cell organisms are tiny and not visible to the naked eye. There are at least 100 trillion bacteria in your body (or around it) at any given moment.
Peptidoglycan is in the cell wall of bacteria. This is an essential component of the cell envelope. This feature can only be found in bacteria.
Finally, if you’ve ever taken antibiotics, then you’d know that bacteria are sensitive to this type of medicine. It’s been specifically designed to destroy or slow down the growth of bacteria.
3. Archaea
Archaea are the oldest of the 3 domains of life. They make up a group of the first organisms to appear on Earth. We know this because they are used to extreme environments like those during the early Earth. For example, Earth was blasted by UV radiation because it hadn’t fully developed an atmosphere yet.
We don’t observe archaea as frequently as bacteria and eukaryotes. This is because they are only found in the harshest environments. For example:
- THERMOPHILES: Thermophiles live in extreme temperatures.
- HALOFILES: Halofiles reside in salty environments.
- METHANOGENES: Methanogenes produce methane gas.
As for their anatomy, Archaea resembles features of both eukarya and bacteria. For example, they are single-cell, have no nucleus, and look like bacteria for structure. Hence their close relation to bacteria.
But they also carry features of eukarya. For example, they don’t have peptidoglycan developed in their cell envelope. On top of that, they are resistant to antibiotics like eukarya. Whereas, antibiotics would flat-out destroy bacteria.
The Domains of Life
There are three domains of life- eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and archaea. These three domains of life have had the most amount of time to evolve, and have been responsible for shaping the world we live in today.
Each of these domains has its unique characteristics, with eukaryotes encompassing complex multicellular organisms, prokaryotes including simpler unicellular organisms like bacteria, and archaea representing a group of single-celled organisms with distinct genetic and biochemical features.
Do you have any questions about this article? Please leave us a comment below and we’d be happy to help.




Dear Earthhow Team,
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990 that divides cellular life forms into three domains, namely Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryote or Eukarya.
Prokaryotic organisms belong either to the domain Archaea or the domain Bacteria.
Please make a correction because the article posted on your website stated that the 3 domains of life are “eukaryotes, prokaryotes and archaea”
References
https://astrobiology.nasa.gov/news/the-three-domains-of-life/
https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Microbiology/Book%3A_Microbiology_(Kaiser)/Unit_1%3A_Introduction_to_Microbiology_and_Prokaryotic_Cell_Anatomy/1%3A_Fundamentals_of_Microbiology/1.3%3A_Classification_-_The_Three_Domain_System
https://www.nature.com/articles/nrmicro2815
As a person whose only class in biology was in 1955, this is new and interesting information, presented in a way that is very understandable. Thank you. I’m currently reading, “Jellyfish, a Natural History”, by Lisa Gershwin in a book club. I need to do a lot of catching up. 🙂
I am getting more interested in the life sciences.
I was looking for this data.