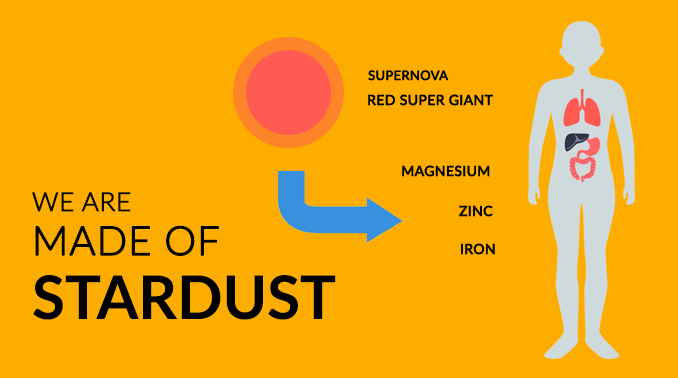
We Are Made of Stardust from Old Supernovas
“How old are the atoms in your body? Most of your body is made of hydrogen and oxygen bonded as molecules of water. That means your body is made up of atoms that are 13.7 billion years old.”
The atoms in your body were created at the start of our universe during the Big Bang. So if you look at it this way, then you’re about 13.7 billion years old.
But your body also has heavier elements like copper and zinc. These atoms were created in the dying stage of an exploding star called a supernova.
These elements were flung into space as dust and gas (stardust). Eventually, they coalesced to become part of a newly forming solar system and our planet Earth.
Because you are made from matter from the Earth, you are made of stardust from old supernovas. So turns out, you are bits and pieces of star and cosmic dust.
Why are stars like element factories?

As we already know, hydrogen and helium have been around since the Big Bang. So stars (like our Sun) take lighter elements like hydrogen and build heavier ones like helium, carbon, and oxygen.
It’s through fusion reaction that stars build elements of their own. But stars can only produce elements as heavy as iron. Anything heavier is made when the star becomes a supernova.
When a star is at the end of its life, its temperature begins to increase. At about 200 million degrees, helium fuses into carbon and oxygen. Then at above 3 billion degrees, it creates silicon, iron, and nickel.
If our sun was bigger, it would go through the process of a supernova. High-mass stars simply don’t burn out of fuel. Instead, it ejects matter violently into space building heavier elements like gold and uranium.
How do supernovas build heavier elements?
Stars larger than our sun go through a faster cycle with more intense pressure. But larger stars have so much energy that they don’t simply die and turn into a white dwarf.
Instead, they expand into a red super-giant and then explode in a dramatic event called a supernova. It blasts material dramatically into space. Eventually, they can then collapse as a neutron star or black hole.
Supernova are important because they form the more complicated elements on Earth from hydrogen to uranium. Supernovas build anything in our periodic table that is heavier than iron.
The process of building heavier atoms than hydrogen is called nucleosynthesis. It happens because neutron gets added into much larger atoms. These are the 92 natural elements, many of which are used to create rocks and minerals.
How do our sun’s fusion reactions work?
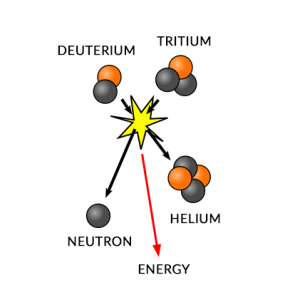
Fusion smashes two or more atomic nuclei together and builds a heavier nucleus. For example, our Sun constantly fuses hydrogen into helium. This process releases energy and sunlight, constantly warming our planet.
When stars like our Sun finish using hydrogen in the core, then it will begin fusing the leftover helium into carbon and oxygen. When this begins, the star will swell up into a red giant.
Based on the initial mass of the star, successive fusion reactions may follow. Starting with hydrogen, it can fuse into helium, carbon, oxygen, neon, silicon, and iron.
If the star has more mass, then it will go further down the chain of reactions all the way up to iron. But if a star has enough mass to fuse iron, it will then supernova once that fusion is complete.
Will our sun ever turn into a supernova?
Like any fire, eventually, they always burn out in the end. Our Sun is no different. It’s at about halfway through its life expectancy with about 4 billion more years remaining.
Our Sun won’t become a supernova and will collapse into a white dwarf. Actually, the vast majority of stars die in a much less violent manner.
This is why we classify it in the lightweight category. Whereas heavyweight stars have the most fuel but burn their fuel at a faster rate.
In general, supernovas are quite rare because stars need to be massive to die this way. After they violently explode, they disperse throughout the galaxy and become part of a newly forming solar system.
For example, our solar system contains elements from different stars which died before our solar system’s existence.

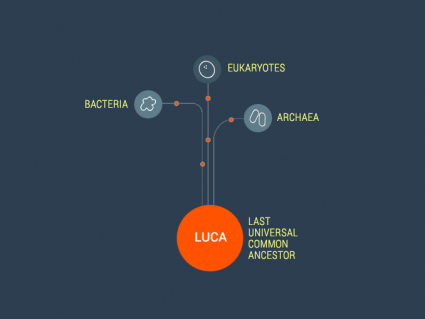


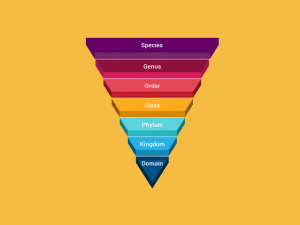
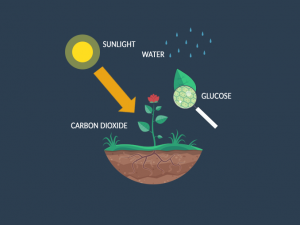
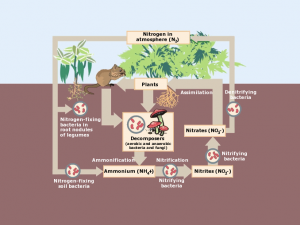
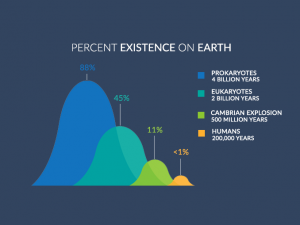
Here’s my best attempt at explaining Earth’s timeline – https://earthhow.com/earth-timeline-geological-history-events/
How were humans created from stardust?