How to Measure the Distance to the Moon
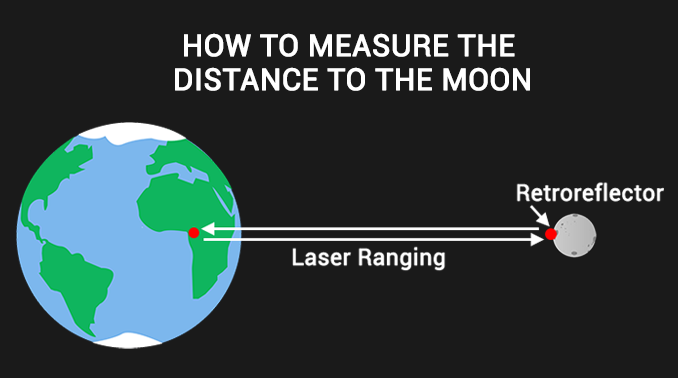
How to Measure the Distance to the Moon
The moon has an elliptical orbit around the Earth so it’s not a constant distance away.
In fact, the moon varies between 225,622 miles and 252,088 miles due to its elliptical orbit. But if you take an average distance, the moon is approximately 238,855 miles (384,400 km).
How do we measure the distance between the Earth and the Moon?
Over time, scientists have found new techniques to measure the distance from the moon to Earth. Each one is more accurate than the next. Find out more below.
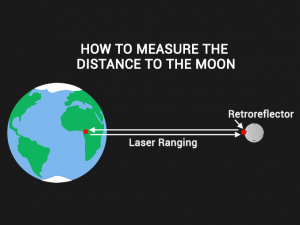
1. Lunar Laser Ranging Experiments
When the Apollo program (11, 14 & 15) astronauts visited the moon, they left retro-reflectors on the lunar surface. When they send a laser pulse to the moon, it reflects off the reflector and back to Earth. And the entire time this pulse is traveling, scientists count the time it takes for it to return.
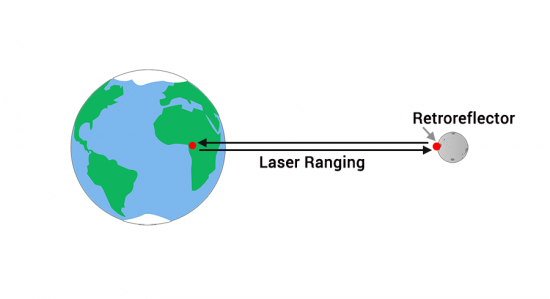
To put this into perspective, light travels at 300,000 km/s. It takes about a second for the light to travel to the moon. Then, it takes another second for it to return. Actually, only a handful of photons come back. So astronomers count how long it takes for those photons to make the journey to the moon.
Currently, the Lunar Laser Ranging Experiments is the most reliable method to estimate the lunar distance. For example, it has exceeded millimeter accuracy involving multiple laser facilities.
2. Radar echoing and lunar distance
Similar to the Laser Ranging Experiments, radar sends a signal and measures how long that echo takes to return. If you know how fast the wave travels, then you can understand distance.
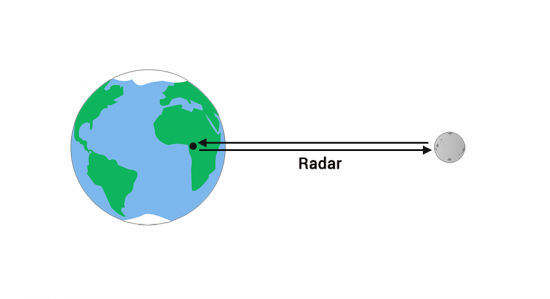
In 1957, a US Naval Research Laboratory broadcasted radar pulses to determine the distance to the moon. After the pulse echoed off the moon, they measured the time it took for the return signal. However, the noise was so high that it couldn’t produce reliable, repeatable measurements.
One year later, this experiment was repeated by the Royal Radar Establishment, in England Using a longer pulse duration, the return echo estimated the moon’s distance as 384,402. Although this was the most accurate lunar distance estimate at the time, it had an error of ±1.2 km.
3. Parallax with two reference points
Astronomers have also estimated the Earth-Moon distance using parallax. For example, you can test out parallax by blinking your left and right eyes back and forth. When you do this, you gain two different vantage points to gain depth perception.
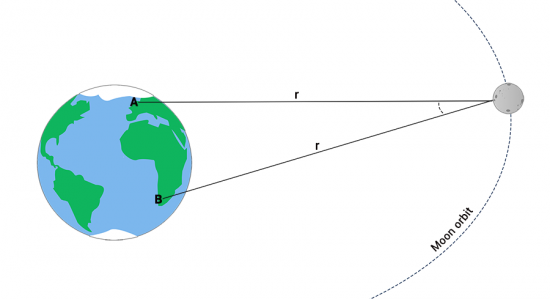
From two different vantage points, both observers take a picture of the moon and compare stars in the background. Knowing the fixed distance between both reference points and orientation, parallax uses triangulation to estimate the distance to the moon based on its apparent shift in positions.
You compare the distance change between both images and measure the parallax angle at two different reference points. With a bit of geometry, you can determine the moon’s distance from the parallax angle from the two views.
4. Earth’s radius and a lunar eclipse
Over 2000 years ago, the Greeks found the circumference of the Earth by looking deep into a well. Eratosthenes estimated the Earth’s diameter was approximately 8,000 miles.
When you hold out a spherical object, Greeks also found through trial and error that a 1-inch diameter object cast a shadow with a length of 108 inches. So if you were to hold up a 1-inch sphere to shield the moon 108 inches away from the eye, it would perfectly block out the sun.
During a lunar eclipse, the Earth shields the moon from the sun’s light. They observed that the Earth cast a full shadow on the moon equal to two-and-a-half-moon diameters. From here, they used the properties of isosceles triangles to formulate that the moon has a diameter of about 2300 miles.
Remember how a 1-inch diameter sphere perfectly blocks the Earth at about 108 inches away from the eye? Finally, they multiplied 108 by 2300 miles to approximate the moon’s distance is about 248,000 miles away.
What is the Distance From the Earth to the Moon?
The moon orbits the Earth and has an elliptical orbit, so its distance is not constant. The average distance from the Earth to the moon is 238,855 miles (384,400 km).
This variation in distance, known as lunar libration, creates subtle changes in the moon’s appearance as it moves closer and farther from Earth in its celestial dance, adding to the wonder of our lunar companion.
Don’t forget.
If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to contact us below in the comment section.









Wow.
Is there any scientific document explaining in more deep the experiment with the laser?
Yes, correct. Surface to surface.
I’m assuming the measurement is surface to surface, correct? Also, make sure to proofread this because it isn’t really clear what was going on when the Greeks estimated how far the moon was.
This thing is a good solar system thing its classical experience opens my mind to know about the moon’s movement to 238,855 miles (384,400 km). This is surprising, shocking, and amazing to hear.
Great article. Needs proofreading. Past tense of cast is cast and 108 inches refers to blocking the Sun or is it the Moon? Either way it is not the Earth which was blocked. The Greeks were standing on the Earth when they made the measurement.