Milky Way Galaxy: 200 Billion Stars and Our Solar System
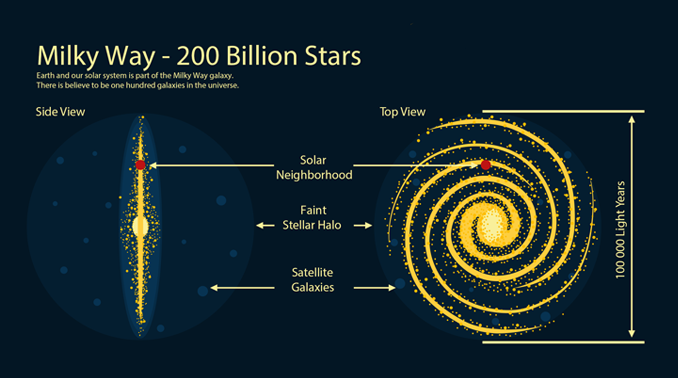
“Earth is in the Milky Way galaxy. It’s home to over 200 billion stars with ours being the sun.”
Not only is the Milky Way a huge accumulation of stars, but it also holds planets, asteroids, meteors, comets, and other solar remnants.
Most stars are at the center of the galaxy with few at the outer edges. A supermassive black hole is at the galactic center.
On the grand scale, the universe holds a mammoth collection of galaxies like the Milky Way. We know this because we observe them using the Hubble Telescope. Galaxies like the Milky Way are rotating around some point in space likely where the Big Bang occurred.
What shape is the Milky Way galaxy?
Galaxies are flat because things that rotate flatten out on the rotational access. For example, Earth is longer at the equator axis because of its rotation. Similarly, most galaxies are similar to the shape of a discus.
Based on their visual appearance, Edwin Hubble developed a classification scheme for galaxies. The three classes of galaxies are:
- Ellipticals
- Lenticulars
- Spirals
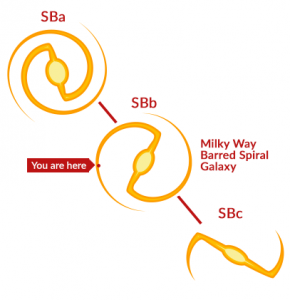
In a clockwise direction, the entire galaxy is rotating as a barred spiral galaxy. The Milky Way is a flattened disk with spiral arms. This disk contains dust, stars, and gas rotating from a center point.
According to the Hubble Galaxy classification scheme, the Milky Way is an SBc barred spiral galaxy. This means that it’s partway between SBb and SBc.
Who are our neighboring galaxies?
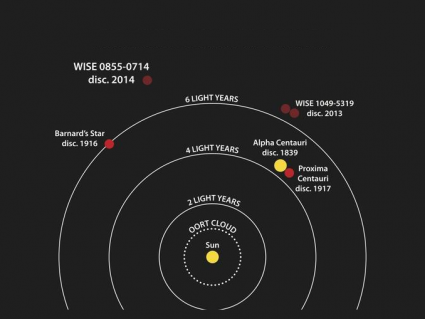
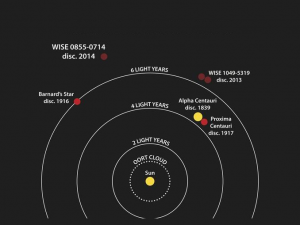
We know the closest neighboring star is Alpha Centauri (Rigil Kentaurus)
ANDROMEDA GALAXY: But the closest galaxy to us is the Andromeda galaxy. This spiral galaxy houses about 1 trillion stars.
So this makes it more than double or even triple the stars compared to the Milky Way.
This galaxy is on a crash course with the Earth due to its gravitational pulls. But no need to panic because this won’t happen for another 4 billion years.
Are there other habitable planets in the Milky Way?
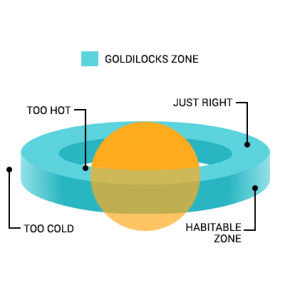
Lucky for us, Earth is in the Goldilocks zone. This means that it’s within the range where liquid water can persist.
In other words, because Earth receives a hearty portion of the sun’s rays, these conditions are “just right” to sustain water and forms of life. Even here in our Milky Way galaxy, at least 10 habitable planets are within the Goldilocks zone.
“Earth’s Doppelgänger might just be in our neighboring star system Alpha Centauri. This means that only light-years away, there is a glimmer of hope that other life can exist.”
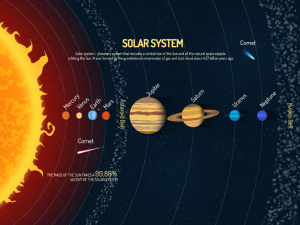
The Milky Way galaxy
Earth is located in the Milky Way galaxy, which has an estimated 200 billion stars. Our sun is one of these many stars and it includes our solar system as well.
Within our vast Milky Way galaxy, the Sun’s gravitational pull governs the motion of the planets in our solar system, shaping the orbits and dynamics that define our cosmic neighborhood.
If you have any questions or comments about the Milky Way galaxy, please do not hesitate to let us know what’s on your mind. We would love to hear from you!





A mammoth error of concept is stated rather early in this article. “Galaxies like the Milky Way are rotating around some point in space likely where the Big Bang occurred.” That is absolutely incorrect. The big bang occured in time, not space. it isn’t a location. It is a past event. Nothing rotates around it because it doesn’t exist anymore. it already happened some 14 billion years ago. And the big bang itself is a theoretical derivation of the observation that our universe has been expanding for a long time. It cannot be observed or even confirmed as that event lies outside our laws of physics, let alone our present universe. Nobody knows what happened at this singularity we call the big bang. Our best ideas all break down if pushed further back than a fraction of a second after that event already happened. Trying to think of all of the galaxies as rotating around a past event is nonsensical even metaphorically. How could we even tell if our universe is rotating? What is it rotating relative to? The singularity is one dimensional so even moving relative to it would lack meaning except in the sense that we are moving away from it in time.
Groups of galaxies move in complex motions that could not be described as a rotation unless we destroy any traditional meaning of that term. What we see is that galaxies group in a weird web of sorts, interconnected like molecules of soap on the surfaces of bubbles in a vast foam. There are enormous voids, some rather spherical, but most often quite irregular between the strands of galaxies. And this foam extends everywhere in all directions into infinity (so far as we can tell).
The cosmology of the supreme structures, the galactic super groups, is fairly well nailed down by a persistently consistent observation of this structure.
If we simplify the model to something our weak minds can process, we can think of the universe as the surface of an expanding balloon, with dots all over that surface all moving away from each other as the balloon is inflated. But we also have to keep in mind that this simplified model is expanding in time, such that there is no location valid for the center of the inside of the balloon. That is all just nothingness left by past events. And this modem greatly simplifies the reality since it renders our three dimensional space as a two dimensional surface.
Even our three dimensions of space is a simplification. There are probably at least five space dimensions but we only really perceive three. Some evidence exists to suggest that there are possibly a lot more dimension.
But the fact that this article has such a fundamentally wrong statement in the first paragraph shows how dumbed down our cosmology has become. The models and simplifications are more pervasive than the complicated and messy truth of our universe, so of course people write articles with the simplifications stated as if they are facts. But galaxies rotating around the big bang is so wrong on so many levels that it isn’t even a simplification. It is just wrong.
I need to get a 200 billion stars name where can I get it?
Does the 200 – 300 billion stars in the Milky Way account for double and triple systems? E.g. Alpha Centauri with its three stars is accounted as one or as three?
A couple of things:
1. You classified the MW galaxy as SBc, when the chart says SBb.
2. The est. size of the MW galaxy ranges from 100 – 200 thousand light-years across. The est. number of stars ranges from 100 – 300 billion.
3. Proxima Centauri is slightly closer to Earth than Alpha, 4.22 – 4.25 for Proxima; 4.35 for Alpha.
4. Our doppelganger (?) orbits Proxima, not Alpha, I understand.