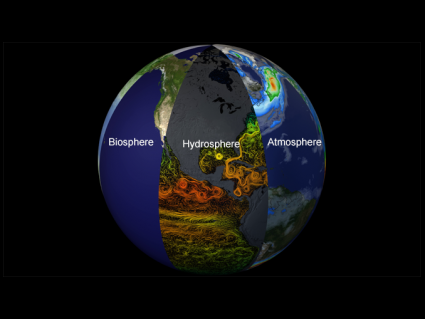
Earth Statistics: Straight-Up Stats of Earth
Measurements
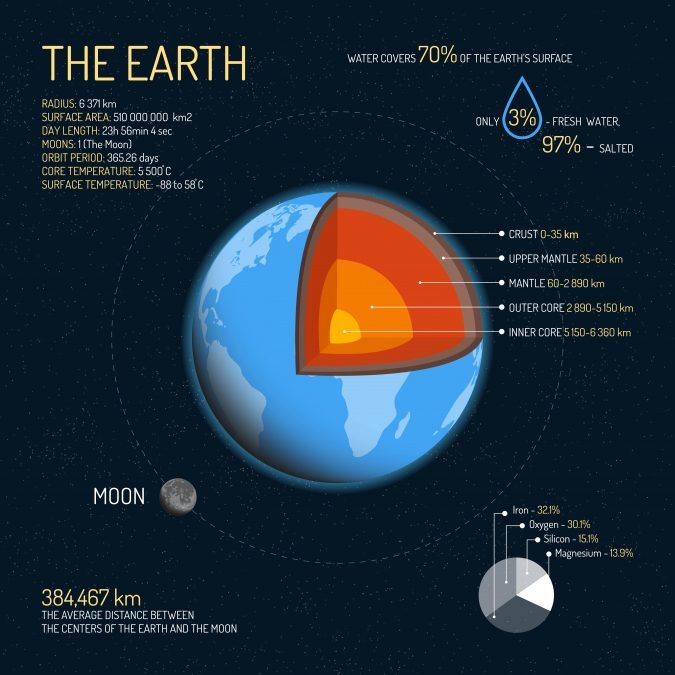
Earth’s radius is approximately 6,371 kilometers, making it the distance from its center to its surface. With a surface area of about 510,000,000 square kilometers and a volume of 1,000,000,000,000 cubic kilometers, Earth is a diverse and vast planet that supports a wide range of ecosystems and geological features.
| Measurement | Value |
|---|---|
| Radius | 6,371 km |
| Surface Area | 510,000,000 km² |
| Volume | 1,000,000,000,000 km³ |
Rotation
Earth has a rotational speed that causes it to spin at approximately 1,600 kilometers per hour, shaping our day and night cycle. The length of an Earth day is approximately 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds, during which the planet completes one full rotation on its axis.
| Rotation | Value |
|---|---|
| Earth spin | 1,600 km/hr |
| Length of Day | 23h 56min 4sec |
Age
Earth is estimated to be around 4.54 billion years old, based on scientific evidence and dating methods. The Earth’s age represents the long and complex history of our planet, including the formation of continents, the evolution of life, and the development of its geological features over billions of years.
| Age | Value |
|---|---|
| Earth’s Age | 4.54 billion ± 0.05 years old |
Distance
The Earth is about 149.6 million kilometers away from the Sun, which is essential for maintaining the habitable conditions on our planet. In contrast, the Moon is much closer, at an average distance of approximately 384,400 kilometers from Earth, influencing tides and lunar phases and serving as a significant celestial neighbor.
| Distance | Value |
|---|---|
| To the Moon | 384,400 km |
| To the Sun | 149,600,000 km |
Water
Water covers approximately 70% of Earth’s surface. This supports life and shapes our climate. Of this vast water supply, about 97% is saltwater found in the oceans, while only 3% is freshwater, which includes water in lakes, rivers, glaciers, and underground aquifers, making it a precious resource for humans and ecosystems.
| Water Type | Value |
|---|---|
| Saltwater | 97% |
| Freshwater | 3% |
Layers
Earth’s structure comprises three main layers: the crust, mantle, and core. The crust, which is the Earth’s outermost layer, ranges from 0 to 35 kilometers in depth, while the mantle extends from 35 to 2,890 kilometers. At the Earth’s center lies the core, reaching depths of 2,890 to 6,360 kilometers. These layers have distinct compositions and properties that influence geological processes and the planet’s overall behavior.
| Layer | Value |
|---|---|
| Crust | 0-35 km |
| Mantle | 35-2,890 km |
| Core | 2,890-6,360 km |
Temperature
Earth’s core, located deep within the planet, has a scorching temperature of around 5,500 degrees Celsius, primarily due to the heat generated by radioactive decay and residual heat from its formation.
In contrast, the surface temperature of Earth can vary widely, with extremes reaching as low as -88 degrees Celsius in Antarctica and as high as 58 degrees Celsius in some desert regions, reflecting the planet’s diverse climates and environments.
| Temperature | Value |
|---|---|
| Core temperature | 5,500°C |
| Surface Temperature | -88 to 58°C |
Shape
Earth’s semi-major axis is approximately 6,378,137.0 meters. This represents the equatorial radius or the longest distance from the Earth’s center to its surface. In contrast, the semi-minor axis measures around 6,356,752.3 meters, representing the polar radius. The semi-minor axis is slightly smaller due to the planet’s oblate spheroid shape.
| Shape Measurement | Value |
|---|---|
| Semi-major Axis | 6,378,137.0 m |
| Semi-minor Axis | 6,356,752.3 m |