5 Major Air Pollution Sources in the Atmosphere
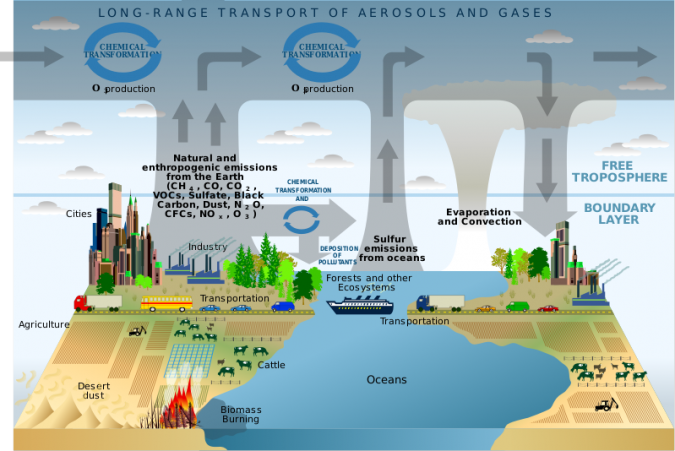
Major Air Pollution Sources
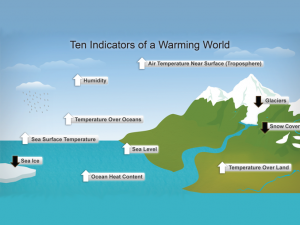
Record temperatures year after year. Our climate is changing so we have to better understand the air pollution sources causing it.
Look at each city in the world. Air pollution ranges from sparkling clean to nasty smog. Why is this the case? It’s because of the air pollution sources they are exposed to.
These are the major air pollution sources in the world:
- Agriculture
- Industry
- Vehicles
- Electricity
- Natural disasters
1. Agriculture Production

Agriculture is a major contributor to methane (80%) (CH4) and ammonia (90%) (NH3). But methane makes up about 9% of total emissions, whereas CO2 makes up about 82%.
METHANE: Methane is a strong greenhouse gas and traps heat more efficiently than other gases. But it’s short-lived because it leaves the atmosphere within a decade after it’s released.
Bacteria in the guts of grass-eating animals such as cattle release methane as a by-product. Industry, landfills, and natural gas systems also generate a significant amount of methane that adds to air pollution.
2. Transportation

Transportation burns gasoline releasing carbon dioxide. Gasoline is carbon bonded to itself or to hydrogen. When a vehicle consumes fuel, it burns these hydrocarbons to generate movement. In turn, it releases water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) as air pollution.
CARBON DIOXIDE: As carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere, it traps heat inside contributing to the effects of greenhouse gas. Transportation accounts for 15%. But with the advances in electric vehicles and cleaner gasoline, is becoming increasingly difficult to account for.
3. Power Generation
Thermal power plants burning high-sulfur coal is a major contributor to greenhouse gases. Not only does it cause air pollution, but sulfur oxides are a risk to health and the environment.
Over time, there has been increasing efficiency in coal use. Overall, thermal power plants have been able to significantly reduce emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants.
4. Industrial and Manufacturing

As developing countries like China and India experience economic growth, they are in a phase of the industrial revolution. This is why cities like Beijing have the highest rates of air pollution and smog in the whole world.
As industry and manufacturing grow, they demand more electricity to power them. Because China uses coal for thermoelectric power plants, higher electricity usage contributes to air pollution.
5. Natural Sources
Finally, there are natural phenomena that release air pollutants into the atmosphere. For example, volcanic eruptions release sulfur and carbon dioxide. Not only can volcano eruptions alter the chemical makeup of the atmosphere, but they are an immediate hazardous risk to human health.
Dust storms also pose a risk to health. For example, sandstorms irritate eyes, skin, and the respiratory system. Dust storms can be caused by desertification.
This is often from overuse of the land, deforestation, or over-grazing. These human activities expose soils and increase evaporation rates on the land.
What are examples of greenhouse gases?
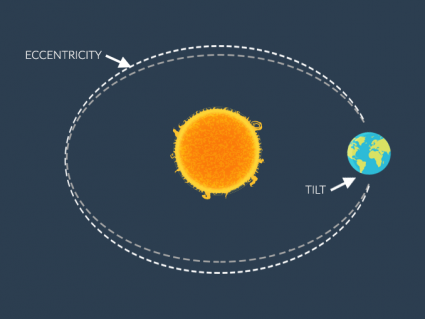
There are natural and human-induced factors that contribute to climate change. When you look back at the history of Earth, climate change has always happened.
- Methane (CH4)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Sulfate (SO4)
- Nitrogen oxide (N2O)
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Nitrate (NO3)
Do you have any questions or comments? Please get back to us in the comment section below.






Not change the subject? But happens to all the carbon black that is release into the ecosystem and the atmosphere? It’s a product used to make all the tires in the world. Where does it go???
Hydrogen was left out. Why?
CO2 is essential to the processes of life on Earth and all of its inhabitants, you are right on that, surely. Although, it is a greenhouse gas like you said, and that means it contributes to heat being held longer in the atmosphere. The abundance of the gas from industry, fossil fuels & vehicle use, and many other sources is what makes the gas toxic and therefore a pollutant because its ratio to water or other life-sustaining properties outweighs the natural amount that keeps the planet at homeostasis. Water vapor carries toxins and partials into the clouds and contributes to acid rain. The ratio of partials to water partials is causing the water to go from a basic pH to an acidic pH, offsetting the natural homeostasis
CO2 is essential to the processes of life on Earth and all of its inhabitants, you are right on that, surely. Although, it is a greenhouse gas like you said, and that means it contributes to heat being held longer in the atmosphere. The abundance of the gas from industry, fossil fuels & vehicle use, and many other sources is what makes the gas toxic and therefore a pollutant because its ratio to water or other life-sustaining properties outweighs the natural amount that keeps the planet at homeostasis. Water vapor carries the toxins and partials into the clouds and contributes to acid rain. The ratio of partials to water partials is causing the water to go from a basic pH to an acidic pH, offsetting the natural homeostasis
If CO2 is a colourless, odourless and non-toxic gas that is essential for plant life (and therefore human and animal life,) why is it being labelled as an ‘air pollutant’ here? I understand that it contributes to the greenhouse effect but water vapour is responsible for the majority of the greenhouse effect, yet it isn’t called a ‘pollutant’.