DNA vs RNA: What’s the Difference?
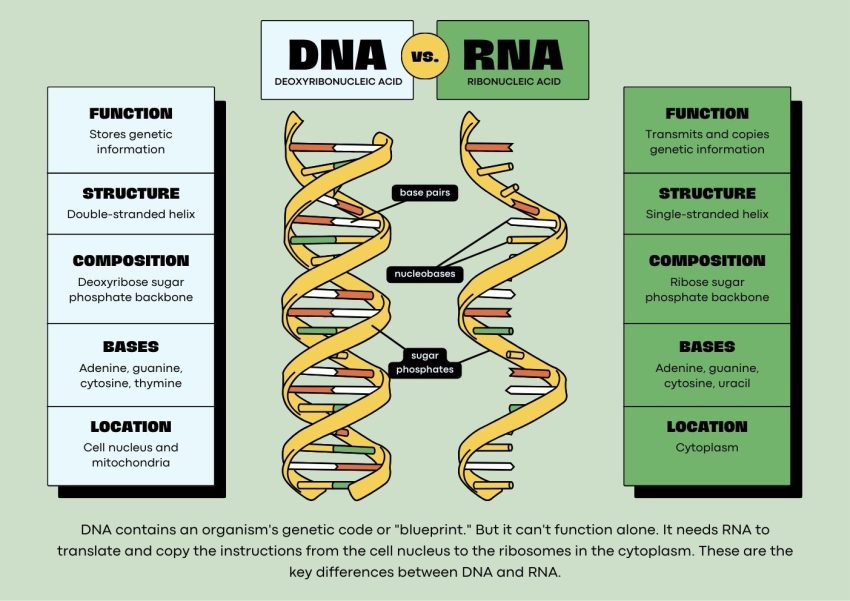
DNA vs RNA. Both are crucial to life, yet they serve different roles in our cells. But what sets them apart? Let’s explore the key differences between DNA and RNA.
Functions of DNA and RNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) acts as the long-term storage of genetic information, while RNA works as a messenger. RNA(Ribonucleic Acid) transmits genetic instructions for building proteins. Unlike DNA, RNA operates in the broader cell environment.
They play a direct role in the assembly of proteins. Furthermore, DNA’s genetic information is passed down to offspring. But RNA’s role is more transient, guiding day-to-day activities within the cell.
| DNA Function | RNA Function |
| Stores genetic information | Transmits genetic messages |
| Guides protein synthesis | Helps in protein assembly |
| Inherited by offspring | Directs cell activities |
Structure of DNA and RNA
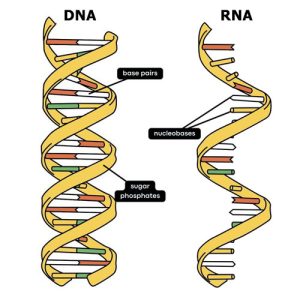
DNA is structured as a double-stranded helix, whereas RNA is typically single-stranded. In DNA, the sugar in its backbone is deoxyribose, while in RNA, it’s ribose.
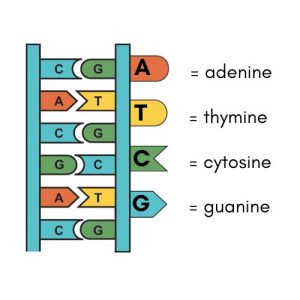
DNA contains the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). But RNA replaces thymine with uracil (U) so it contains A, U, C, and G bases.
This substitution of thymine with uracil in RNA allows eukaryotic cells to efficiently transcribe and translate genetic instructions into functional proteins.
| DNA Structure | RNA Structure |
| Double-stranded helix | Single-stranded |
| Made of deoxyribose sugar | Made of ribose sugar |
| Contains A, T, C, G bases | Contains A, U, C, G bases |
Location of DNA and RNA
DNA is mainly located in the cell nucleus and remains there, forming the structure of chromosomes. In contrast, RNA is found both in the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and it can move between these two areas.
While DNA stays in a fixed location, RNA is more mobile, functioning in various parts of the cell. RNA’s mobility and versatility make it an essential player in processes such as transcription.
| DNA Location | RNA Location |
| Primarily in the cell nucleus | Found in the nucleus and cytoplasm |
| Stays within the nucleus | Moves between nucleus and cytoplasm |
| Forms chromosomes | Exists as single strands or folded structures |
Origin of DNA and RNA
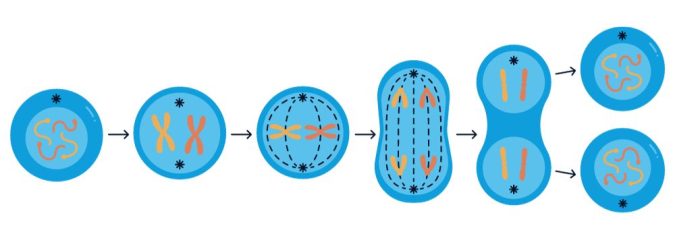
DNA originates from the replication of parental DNA. It’s passed down through generations with a consistent sequence during cell division (Mitosis).
In contrast, RNA is synthesized from DNA, using it as a template in a process called transcription. Unlike DNA, which maintains stability over generations, RNA is continuously produced and degrades within the cell.
| DNA Origin | RNA Origin |
| Originates from parental DNA | Synthesized from DNA as a template |
| Replicated through cell division | Formed through a process called transcription |
| Maintains consistent sequence generation to generation | Continuously produced and degraded in the cell |
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA are two fundamental molecules in the world of genetics. Each has its unique characteristics and roles.
First, DNA serves as a stable, long-term storage of genetic information. Also, it plays a central role in inheritance and is passed down to offspring.
Whereas RNA is more versatile. It acts as a messenger and catalyst in various cellular processes like protein synthesis.
Understanding their structure, composition, and location helps us learn about the intricacies of genetics and the complexity of life itself.