What Do Meteorologists Do?

What Is a Meteorologist?
Storm chasing, withstanding a direct hit from a tornado or setting foot in front of a giant tsunami… These things usually do not accompany the job description of a meteorologist.
But understanding atmospheric chemistry and physics, including how they relate to weather and climate patterns usually is important.
If you’re fascinated by weather and climate, then maybe you want to pursue a meteorologist career.
So, let’s take a look at 5 reasons why you should and shouldn’t pursue a meteorologist career.
How much do meteorologists earn?
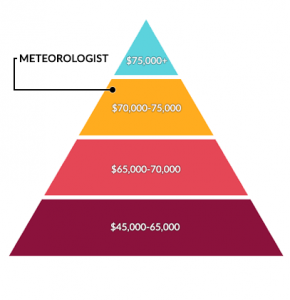
Salaries can range significantly for meteorologist careers in the low to high range.
But on average, the median salary is about $79,400 with entry-level positions much lower. On average, this is much higher than other environmental science careers.
Job opportunities are mostly in government, education, and the private sector. For example, news stations hire meteorologists to report the weather.
Over the years, demand for “operational forecasters” has declined because of the usage of computers and predictive modeling. There is value to be had by a seasoned weather forecaster but job opportunities have become rarer.
What do meteorologists do?
The best thing about being a meteorologist is that they can continually be wrong and keep their job. In fact, this happens on a day-to-day basis for weather forecasting.
The research in forecasting storm systems/ significant weather events can involve some serious number crunching. If math is not your thing, then weather still have a community of hobbyists to be a part of.
This is why sharpening your math skills is a pro tip for meteorologists. If you’re not good at it and you want to be a meteorologist, you need to get good.
Forecasting weather events could take one or several hours depending on the complexity of the system.
You’d be surprised at how applicable meteorology is to so many situations and as a professional how easy it often is to cut through complex problems.
What can you expect working as a meteorologist?

If you land a meteorologist career, it’s often an unpredictable and challenging job. It’s never what you think it will be. You will partake in weather prediction and issue warnings for severe weather.
The weather forecasts you create affect businesses, sporting events, and people’s daily lives.
Meteorologists work at weather stations, in the field, office, or laboratory and are often subject to longer work hours for weather emergencies.
For example, winter hours can bring longer days because of blizzards and snowstorms. Depending on location, your situation will be unique according to our seasonal patterns.
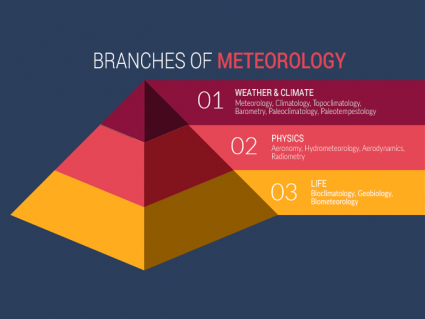
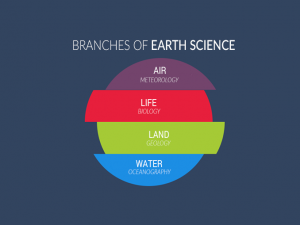
It’s necessary to understand how water and climate relate to the branches of meteorology.
Who do meteorologists work for?
Operational meteorologist careers are often highly desirable jobs. But the downside is that they are very competitive too.
For example, it’s common for some National Weather Service (NWS) job postings to have hundreds of applicants
But there are jobs in the private sector, research jobs within schools, and broadcasting jobs. Nevertheless, these jobs are still competitive but to a lesser degree.
After graduation, finding a decent-paying job can be challenging and is completely based on supply and demand.
Do meteorologists require a degree or certification?

Some of the most common degrees for meteorologists are in atmospheric science, climate studies, and meteorology. A lot of the entry position requirements are a Bachelor’s Degree in meteorology.
But a Masters or Ph.D. are options to enhance employment opportunities and salary. Meteorologists are often grouped with climatologists and atmospheric scientists.
Experience goes a long way. It’s important to learn all the ins and outs of a meteorologist career. Expanding your knowledge in this profession is what counts the most to get ahead of the curve.
What Do Meteorologists Do?
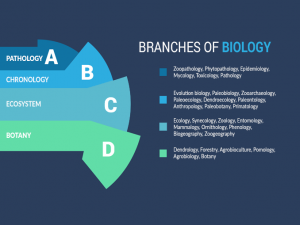
Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere and how it interacts with other types of weather. It is a field that can include atmospheric chemistry, climatology, environmental science, cloud physics, astronomy, and geography.
The meteorologist is the key player in the weather forecasting community. They are responsible for public safety and broadcast warnings of severe weather, as well as other forecasts.
If you have any questions about meteorologists or the field in general, please let us know with a comment below.