33 Branches of Biology: A Comprehensive Outline
“The branches of biology are plentiful. Biology works with time, disease, ecosystems, and even extraterrestrials. It also works on different scales. From individual atoms to the entire biosphere, biology is a diverse field of study.”
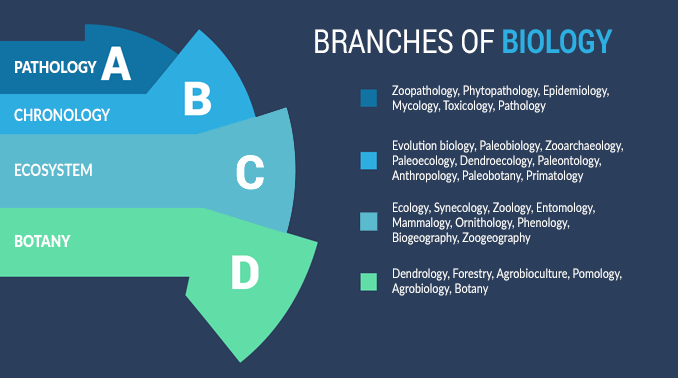
We divide the branches of biology into the following fields:
- BIOLOGY: How life and living organisms are structured, distributed, originated, evolved, and function.
- CHRONOLOGY: How biology originated, evolves, and will adapt as a function of time.
- ECOSYSTEM: How living organisms interact with the physical environment.
- BOTANY: How plants are classified, grow and are managed in nature.
- PATHOLOGY: How disease spreads and interacts with living organisms.
- ASTROBIOLOGY: How life in the universe originated, evolved, and its ultimate fate.
Pathology
Pathology is a whole field dedicated to how diseases spread. For example, phytopathology examines how diseases spread and are managed by plants. In contrast, the focus of zoopathology is on animal disease spread and prevention.
On a large scale, epidemiology looks into how disease and determinants of health are transferred and distributed in populations. For example, an epidemiologist models a disease outbreak and prevents its spread.
Often, toxicology deals with how individual organisms are affected, treated, and diagnosed by poisonous substances. It’s common to test in a laboratory the various substances and materials.
- ZOOPATHOLOGY – How animal disease spreads and is prevented.
- PHYTOPATHOLOGY – How diseases spread and are managed for plants.
- EPIDEMIOLOGY – How disease and determinants of health are transferred and distributed in populations.
- MYCOLOGY – How fungi are studied including chemical, physical, and taxonomical properties.
- TOXICOLOGY – How living organisms are affected, treated, and diagnosed by poisonous substances.
Chronology
Some fields of biology work with time. For example, ‘paleo’ relates to the past. Over a geologic time scale, biology studies plants (paleobotany), animals (paleozoology), and general organisms (paleoecology).
Evolution biology is one of the most popular branches of biology. It focuses on how life originated, evolved, and will transform in the future. For example, primatology makes the connection between primates and humans.
Anthropology is different from paleontology because of its main focus. While anthropologists study how humans and societies behave, paleontologists are primarily concerned with animal and plant fossils.
- EVOLUTION BIOLOGY – How living things change over time and how life originated.
- PALEOBIOLOGY – How prehistoric life and fossils were composed specific to a geologic time scale.
- PALEOECOLOGY – How organisms interact in environments over a geologic time scale.
- PALEOZOOLOGY – How multicellular animal fossils are used to reconstruct prehistoric environments.
- ZOOARCHAEOLOGY – How animal remains are used to explore interactions between people, animals, and the environment.
- PRIMATOLOGY – How probate behavior evolved often linking human and primate characteristics.
- PALEOBOTANY – How plant fossils can reconstruct past environments in geologic time.
- DENDROECOLOGY – How tree rings are used to investigate forest development, disturbance areas, and environmental change.
- ANTHROPOLOGY – How humans and societies behave from past, present, and future.
- PALEONTOLOGY – How plant and animal fossils are used to trace life and investigate the origin of species.
Ecosystem
The ecosystem works together as a collection of different parts. These interactions between the physical environment and living organisms are ecology.
Living organisms can be broken up further into insects (entomology), birds (ornithology), and mammals (mammalogy). And phytogeography and zoogeography best understand how plants and animals are distributed in geographic space.
Phenology involves meteorology to understand botany. More specifically, it inspects seasons and cyclical climate patterns that influence plant and animal species.
- ECOLOGY – How organisms relate to each other in their physical environment including distribution and population dynamics.
- SYNECOLOGY – How specific groups of animal and plant species relate within a community.
- ZOOLOGY – How animals evolve, are classified, interact, and are distributed.
- ENTOMOLOGY – How insects are classified and categorized.
- MAMMALOGY – How mammals are characterized including anatomy, taxonomy, and natural history.
- ORNITHOLOGY – How bird species are distributed, behave, and described with a focus on conservation.
- PHENOLOGY – How seasons and cyclical climate patterns influence plant and animal species.
- BIOGEOGRAPHY – How ecosystems are distributed in geographic space.
- ZOOGEOGRAPHY – How animals are distributed in geographic space.
Botany

The main focus of botany is plant science. Botany looks at how plants are classified and how they grow in nature. Botany is synonymous with plant science or phytology.
Forestry is specific to how trees are managed, planted, conserved, and cut down. Alternatively, dendrology narrows down how trees are managed, planted, conserved, and cut down.
Meanwhile, arboriculture studies how individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other woody plants respond to cultural practices in the environment.
- BOTANY – How plants grow and are classified.
- FORESTRY – How trees are managed, planted, conserved, and cut down.
- DENDROLOGY – How woody plants and tree species are identified.
- PHYTOGEOGRAPHY – How plants are distributed in geographic space.
- ARBORICULTURE – How individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants are cultivated, grow, and respond to cultural practices in an environment
- AGROBIOLOGY – How crop production can be improved through plant nutrition.
Astrobiology
The main focus of astrobiology is how life in the universe originated. Instead of life on Earth, astrobiology considers extraterrestrial life forms and the ultimate fate of the universe.
If you want to pinpoint the possibility of life in space, exobiology estimates how likely life exists on other planets. If there are extraterrestrials, it also considers how to detect them.
Lastly, astrochemistry involves studying substances outside of Earth. For example, it answers what is the chemical makeup of celestial bodies, stars, and interstellar space, and how it relates to life in the universe.
- ASTROBIOLOGY: How life (including extraterrestrials) in the universe evolved, originated and what will be its fate.
- EXOBIOLOGY: How likely and where is life in space.
- ASTROCHEMISTRY: How to study substances in celestial bodies, stars, and interstellar space.



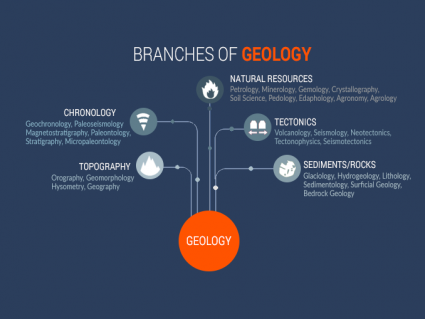


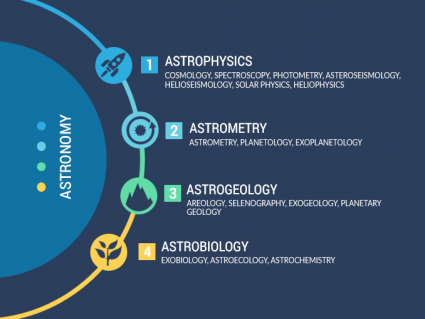
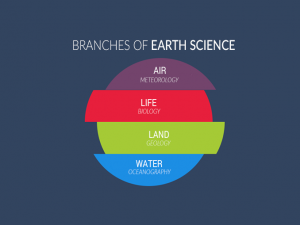






thank you I knew there are more than 3 branches of biology
Outstanding outline!