10 Roles of a River: Beyond Our Waterways

What Are the Roles of a River?
Rivers are dynamic and essential. Plus, they fulfill diverse roles in our world.
Today, you’ll learn the significance of a river is far-reaching.
Let’s explore the contributions of rivers in this brief overview.
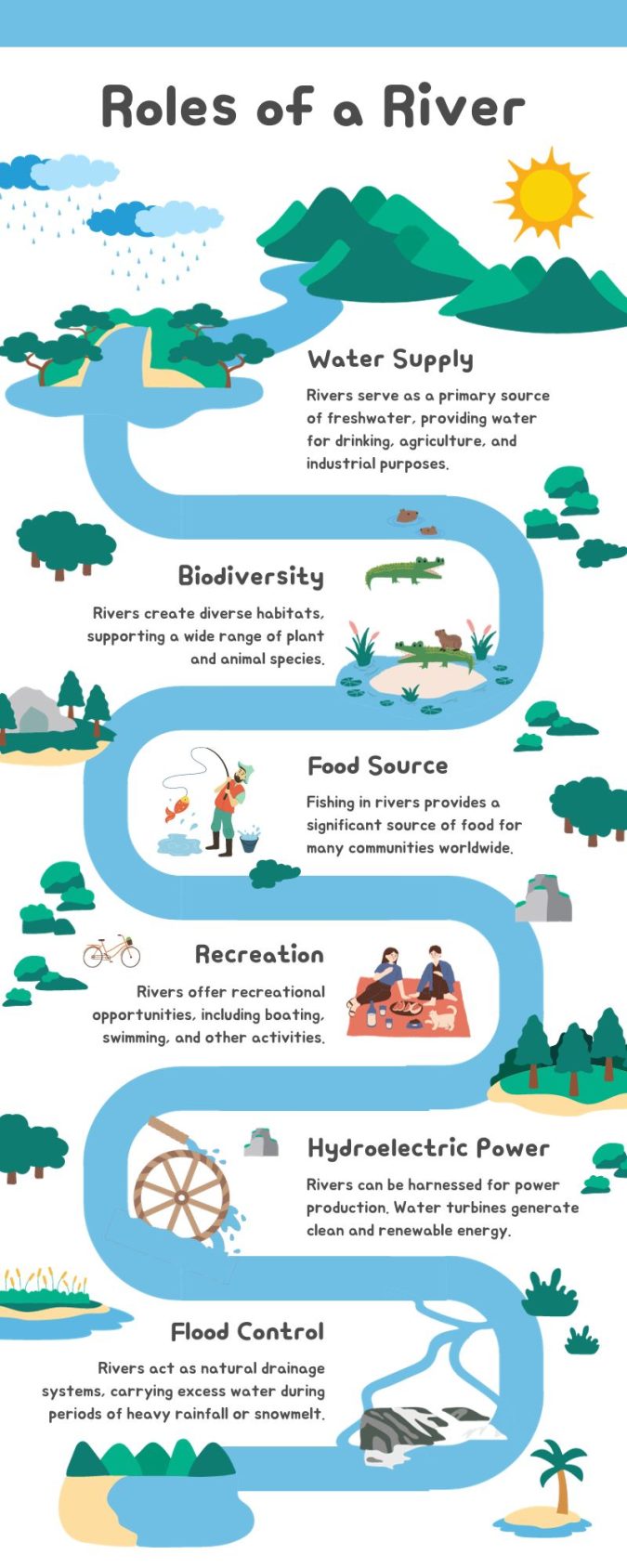
1. Water Supply

Rivers serve as vital sources of freshwater, supplying water for various human, animal, and plant needs. Without rivers, a lot of habitats wouldn’t be able to survive.
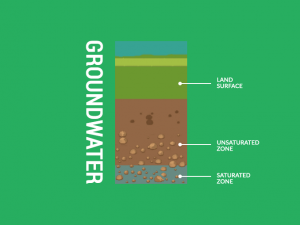
Although groundwater is a source of water, rivers also supply essential freshwater for communities worldwide. Moreover, they act as lifelines for communities, sustaining agriculture, industry, and ecosystems.
2. Biodiversity

River ecosystems provide diverse habitats, supporting a variety of plant and animal species. It also contributes to the intricate web of biodiversity and contributes to ecological balance.
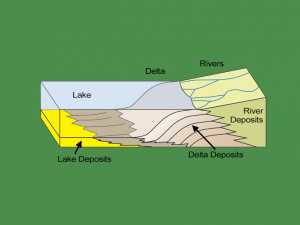
Consider the Mississippi River Delta as shown in this map. Marshes, swamps, and waterways create a rich ecosystem. This supports various plant and animal species, from migratory birds to various fish.
3. Food Source

Fishing in rivers is a source of food for communities worldwide. Additionally, river fisheries contribute to local economies and cultural traditions.
Some fish, like salmon, show anadromous behavior. This means they migrate from the ocean to freshwater rivers to spawn. These incredible journeys can span thousands of miles as part of a salmon’s lifecycle.
4. Recreation

Rivers provide recreational activities such as fishing, boating, and rafting. All contribute to tourism and provide visitors with the experience of seeing the natural beauty of a river environment.
In some cases, river fishing has led to the development of unique cultural practices. For example, some communities have fishing traditions that they pass down through generations.
READ MORE: Stream Ordering and the Strahler Method
5. Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric generators harness the power of moving water and are a tremendous source of energy. After coal and natural gas, it’s the 3rd major electricity source in the world.
Harnessing the energy of flowing rivers not only provides electricity production but also is a renewable source of electricity. Hydroelectric power has been paving the way for a more environmentally friendly electricity landscape.
6. Flood Control
Rivers act as a natural drainage system within their watershed. Their role is to carry water during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt.
This natural drainage prevents flooding by transporting excess water away from higher elevations. A network of rivers helps maintain hydrological balance. This can also mitigate the impact of extreme weather events.
7. Transportation

Historically, rivers served as important transportation routes for trade and travel. For instance, the Nile River enabled the movement of goods in ancient Egypt.
While a river’s role in transportation has evolved, their significance as trade routes remains important. This is because they shaped early human civilizations such as in Egypt.
8. Irrigation
Rivers are important for serving as a reliable water source for agricultural purposes. Through the construction of canals, water from rivers is diverted to fields.
These irrigation canals can support crop growth and ensure agricultural productivity. Rivers can also transport nutrients, contributing to the fertility of surrounding lands.
9. Cultural Significance

Many cultures have strong connections to rivers. For instance, the Ganges River holds immense cultural significance in Hinduism. It is revered as a sacred river, and millions of people participate in rituals and ceremonies along its banks.
Native American tribes in North America view rivers as sacred. For example, the Missouri River is considered sacred by the Lakota Sioux. Additionally, various tribes attribute cultural importance to specific rivers within their traditional territories.
10. Erosion and Sediment Transport

Rivers play a key role in eroding rocks and transporting sediments. Over time, this shapes landscapes, carving out valleys, canyons, and other geological formations.
For example, the Colorado River has been a significant force in shaping the iconic landscape of the Grand Canyon. It’s through erosion and sediment transport. This is how rivers showcase the transformative power of rivers over geological epochs.
“A river cuts through rock, not because of its power, but because of its persistence.”
Jim Watkins
A River Runs Through It
Rivers are serious forces in our natural world. These are the 10 longest rivers in the United States.
Rivers shape landscapes and support ecosystem health. Their significance spans cultural, economic, and environmental dimensions.
Rivers are interconnected with the well-being of both nature and society.
Rivers play a vital role in maintaining a balanced and healthy environment over the long term.