River Delta: How It Forms
“River deltas form when streams and rivers carry too much sediment clogging the entrance into the basin. Because increased sediment builds up, this forces the basin entrance to widen forming a delta.”
What is a river delta?
River deltas form through a complex and dynamic process involving the interaction of rivers, sediment, and the forces of waves, tides, and ocean currents.
Deltas take different shapes. For example, if you have too many sediment deposits in excess, a feature like a bird-foot delta forms.
Let’s review the anatomy of how river deltas form.
How does a river delta form?
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how river deltas typically develop:
- River Flow: It all starts with a river, usually a major one, carrying a significant amount of sediment from its upstream sources. This sediment includes sand, silt, clay, and organic material. Stream ordering can influence the size and formation of river deltas at its mouth.
- Slowing Down: As the river nears its terminus (where it meets another body of water, such as an ocean or sea), its velocity decreases due to the flattening of the landscape and the influence of gravitational forces.
- Sediment Deposition: With reduced flow velocity, the river can no longer carry all the sediment it has transported from upstream. Consequently, it starts depositing this sediment as it enters the calmer waters of the coastal area.
- Channels and Distributaries: As sediment accumulates, it begins to block the main river channel. This causes the river to split into smaller channels known as distributaries. These distributaries carry sediment-laden water in different directions across the coastal plain.
- Sediment Build-Up: Over time, sediment continues to be deposited along the distributaries, creating a network of interconnected channels. The sediment piles up, gradually building the delta. The highest sediment accumulation usually occurs near the delta’s mouth.
- Delta Formation: The interplay of river discharge, tides, waves, and ocean currents influences the shape and growth of the delta. Deltas can take various forms, including bird’s foot, arcuate, and cuspate, depending on these environmental factors.
Deltas are fertile and often overcrowded

When an area floods, sediments spread across the region. When water recedes, soils are rich and fertile for agricultural purposes.
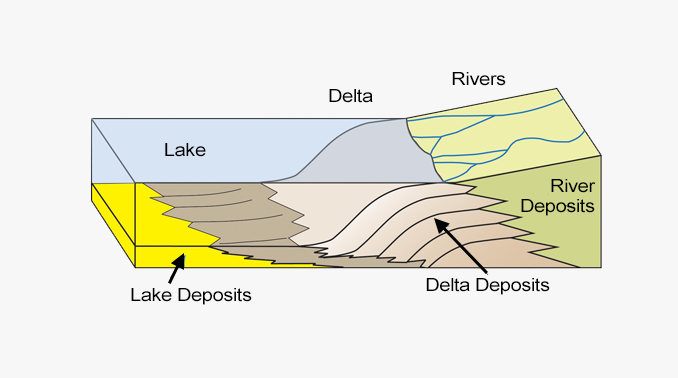
In this diagram, the river enters a lake. The water flow decelerates and loses energy with sediments dropping in. A delta forms depositing a prism of sediments that gradually tapers out toward the lake interior.
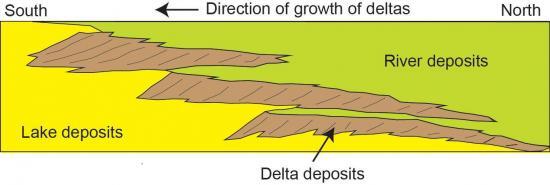
Throughout geologic time, deltas deposit layers upon layers of sediment. For example, the diagram below depicts a vertical cross-section through geological layers deposited by rivers, deltas, and lakes.
Deposits from a series of successive deltas build out increasingly high in elevation as they migrate toward the center of the basin.
How River Deltas Form
The river delta is a landform that occurs when a river enters an ocean, lake, or another river. The shape of the river from the point where it enters the water to the mouth of its tributary with its mouth in the mainstream is generally triangular in cross-section.
This shape has been created by the nature of flowing water, which creates the shape of a triangle along its pathway. This demonstrates the role of a river in shaping the land through erosion and deposition.
As always, please use the comment form below to get in touch with us for further information on river deltas or any related topic.



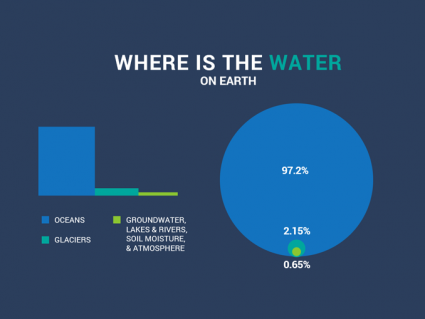




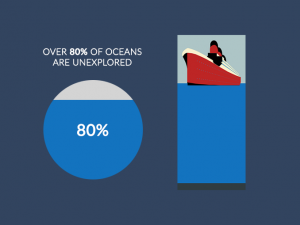
It’s good and helpful.
Hi I am very interested in geography, because my aim is to become a geologist in my future. And I am dreaming about how I will study the earth structure and also study atmospheres.