Pangea Fossils: Evidence of the Pangaea Supercontinent
At one point in time, all continents were merged together as one supercontinent “Pangea”. We’ve used fossil evidence to know continental drift exists.
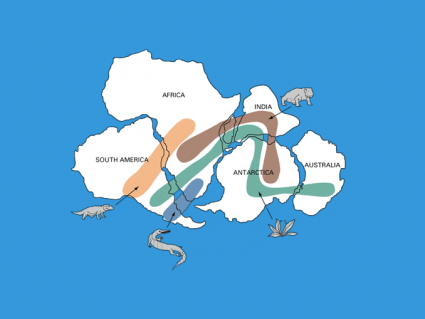
At one point in time, all continents were merged together as one supercontinent “Pangea”. We’ve used fossil evidence to know continental drift exists.
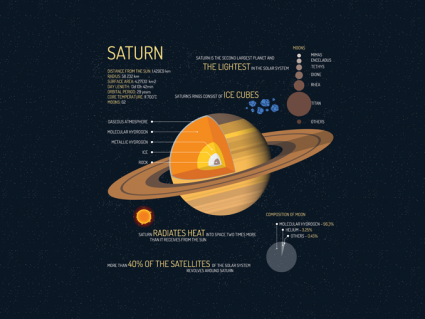
We all know planet Saturn for its iconic rings. But there’s more facts about Saturn like its weather, Titan and its the lightest planet in the solar system.
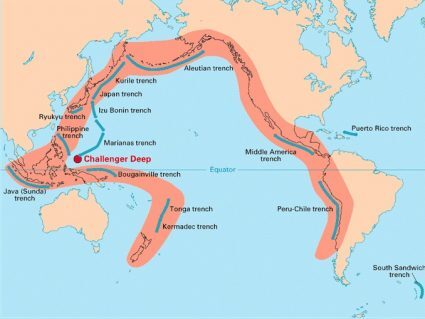
The Pacific Ring of Fire has the most active chains of volcanoes in the world. This is because tectonic plates collide and sink at these zones of subduction.
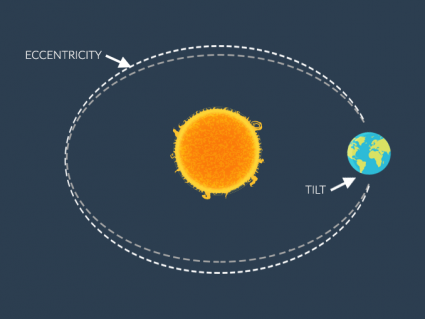
Earth revolves around the sun in a roughly circular orbit. But about every 200,000 years, its orbit becomes more eccentric because of the Milankovitch Cycle.
Beneath the oceans, lava erupts every day from mid-oceanic ridges. These divergent plate boundaries pull apart from each other creating new igneous rock.
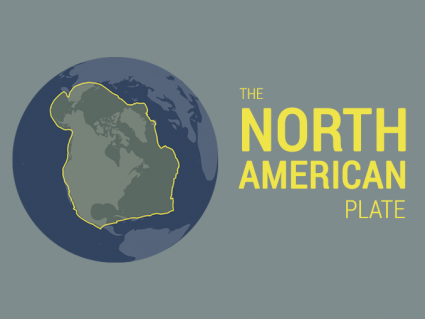
The North American plate extends all the way over the North pole to Siberia. It also includes Greenland, Cuba, the Bahamas and part of the Atlantic Ocean.
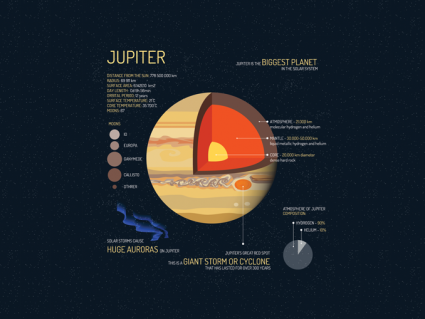
The gas giant known as Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. Other interesting facts include its 79 moons, weather patterns and huge auroras.

When it rains, water zig-zags all the way through a tributary system to a river or lake. Like an upside-down umbrella, a watershed catches all rain water.

When the moon is close to Earth, its gravitational pull stretches the side it’s facing. Because oceans hold a set amount of water, levels rise in one area.
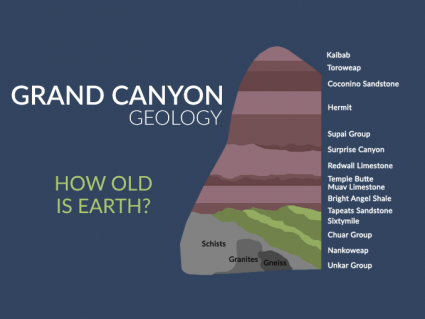
Like a stack of pancakes, younger rock layers pile on top of older layers. We use the law of superposition to reveal Earth’s age and Grand Canyon geology.
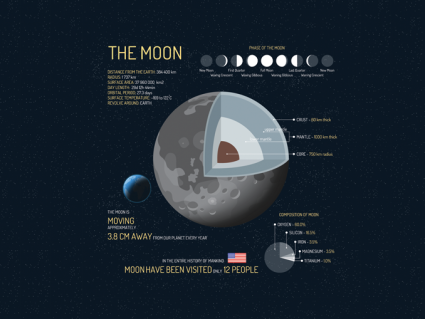
Earth’s moon was formed at the same time that Earth did. Interesting moon facts include its gravity is 1/6 of Earth and temperature range of -173°C to 127°C

The giant impact hypothesis models the formation of our moon. It starts with a Mars-sized object hitting Earth. This object (moon) still remains in orbit.

What makes Earth unique is its ozone layer. Ozone is a colorless gas made up of three oxygen atoms which protects us from harmful UV radiation from the sun.
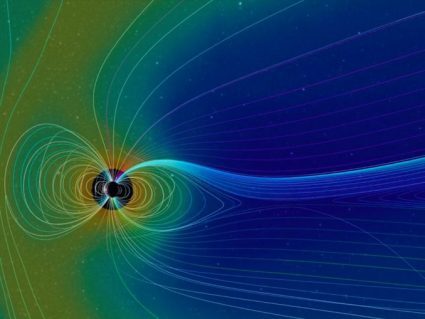
Charged particles or plasma makes up about 99% of the universe. Magnetic reconnection involves how this plasma interacts with magnetic fields (like Earth’s)
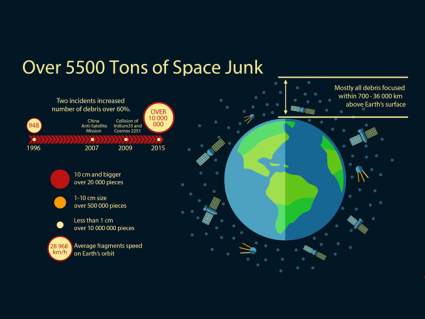
There is over 5500 tons of space junk above Earth’s surface. They mostly consist of small and medium debris within 700 – 36,000 km range in the atmosphere.