Entomologists: Experts in Insects

What Does an Entomologist Do?
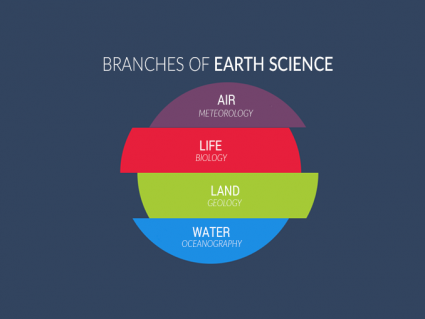
Entomologists study insects, including how they live and grow. Because insects are everywhere, they learn how they help or harm us. While doing this, they also help protect our environment and contribute to biodiversity.
Are you looking to become an entomologist? Here are some of the top specializations in entomology that exist today:
1. Forensic entomology
Forensic entomology is the study of insects on dead bodies to solve crimes. By looking at bugs, forensic entomologists can tell the time of death. For example, if flies are found on a body, forensic entomologists can estimate how long the person has been dead.

2. Medical entomologist
A medical entomologist studies insects that affect human health. They research how bugs spread diseases to people. For instance, a medical entomologist might study mosquitoes to find ways to stop them from spreading malaria.
3. Agricultural entomologist
An agricultural entomologist studies insects that affect crops and farm animals. While finding ways to protect food production from pests, they help farmers grow food productively.
4. Forest entomologist
A forest entomologist studies insects that live in forests. They may work with foresters and look at how these bugs affect tree health. For example, a forest entomologist might study bark beetles to prevent them from damaging large areas of forest.
Famous Entomologists
Looking to be an entomologist? Join the ranks of famous entomologists. Here’s a list of some of the most famous entomologists and their accomplishments in the field:

Justin O. Schmidt
Justin O. Schmidt is an entomologist known for creating the Schmidt Sting Pain Index. This index ranks the pain of insect stings from various species on a scale from 1 to 4. His work has also helped us understand the defensive strategies of stinging insects.
May Berenbaum
May Berenbaum is a renowned entomologist and professor at the University of Illinois. She’s known for her research on how insects adapt to chemical defenses in plants. Berenbaum has also been a leading voice in raising awareness about the decline of bee populations.
Charles Valentine Riley
Charles Valentine Riley was a pioneering entomologist in the late 19th century. He made contributions to the field of agricultural entomology by using biological control to manage pests. Riley is celebrated for his work in saving the French wine industry from the grape phylloxera pest.
How Much Do Entomologists Earn?
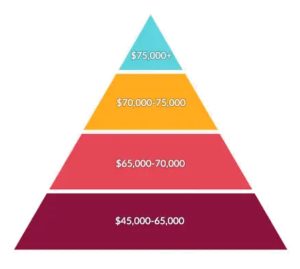
The average salary for an entomologist in the United States is around $63,000 per year. But an entomologist can earn anywhere in the range between $40,000 and $90,000 a year.
Generally, entomologists working in research, academia, or government might earn differently. Those working for private companies, especially in biotechnology or pharmaceuticals, might earn more.
But you also have to look at experience and location. Entomologists with advanced degrees or specialized expertise can receive higher salaries. Finally, entomologists working in urban areas often have higher salaries.
Is There a Degree in Entomology?

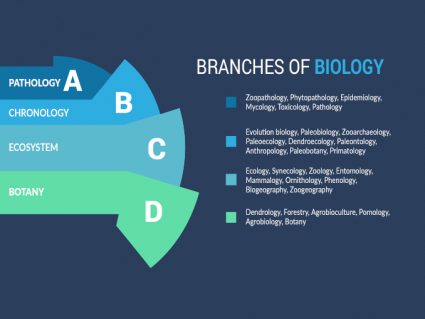
Does an entomology degree exist? Yes, this type of degree exists. Many universities offer bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees in this field. It’s typically a specialized program and branch of biology.
In a bachelor’s program, students learn about insect biology, ecology, and control methods. A master’s or doctoral degree allows for more specialized research. For example, there are areas like pest management, insect behavior, or ecological impact.
These advanced degrees often lead to careers in research or academia. Plus, it includes specialized roles in agriculture or public health. So, for anyone interested in studying insects, pursuing a degree in entomology is a great path.
What Is an Entomologist?
Well, that wraps things up for today. Choosing a career as an entomologist is unique. It allows you to explore the world of insects and their impact on us.
Who knows what path it might take you on? Could it be the environment, agriculture, or health? It depends on where you want to take it
Do you have any questions about entomology? We’d love to hear from you in the comment section below.