Ozone Layer: Earth’s Protective Shield Has a Hole In It
What makes Earth unique is its ozone layer. Ozone is a colorless gas made up of three oxygen atoms which protects us from harmful UV radiation from the sun.

What makes Earth unique is its ozone layer. Ozone is a colorless gas made up of three oxygen atoms which protects us from harmful UV radiation from the sun.
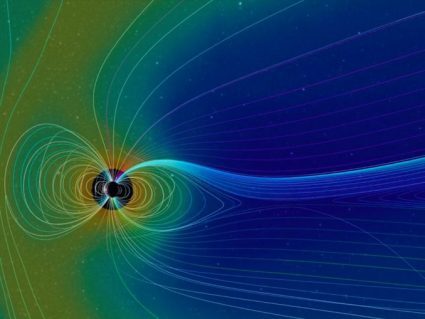
Charged particles or plasma makes up about 99% of the universe. Magnetic reconnection involves how this plasma interacts with magnetic fields (like Earth’s)
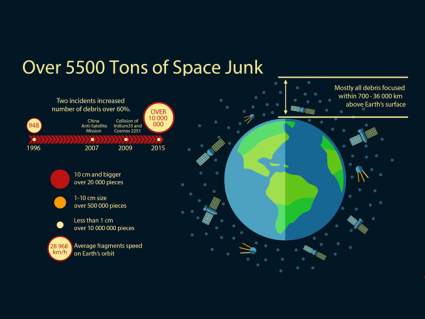
There is over 5500 tons of space junk above Earth’s surface. They mostly consist of small and medium debris within 700 – 36,000 km range in the atmosphere.

During magnetic storms, trapped plasma flashes lights that are observable around the globe. This disturbance in the magnetosphere is the Aurora Borealis.

The magnetic field gives us a layer out in space called the magnetosphere. Without it, Earth would be exposed to solar and cosmic radiation.
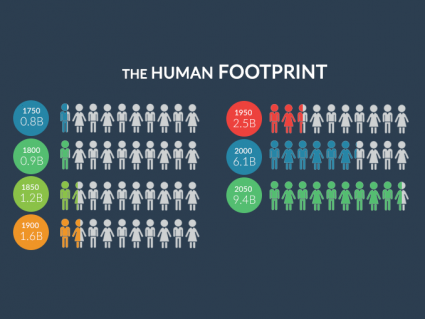
In flesh and blood, 7.6 billion humans live on Earth. The emergence of humans has left a profound impact. The demand for resources is the human footprint.
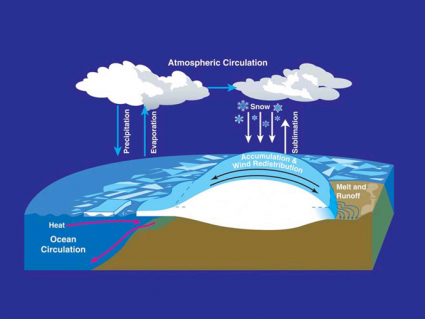
Climate feedback loops either amplify or reduce climate change. Positive feedback loops like permafrost melt amplifies climate change because it releases methane.

Lightning is hotter than the sun, it strikes 8.6 million times a day and more lightning facts. Because when there’s thunder, there’s sure to be lightning.

The Earth is a big magnet. This is why compasses point to the magnetic north. But north didn’t always point northward because of magnetic pole reversals.
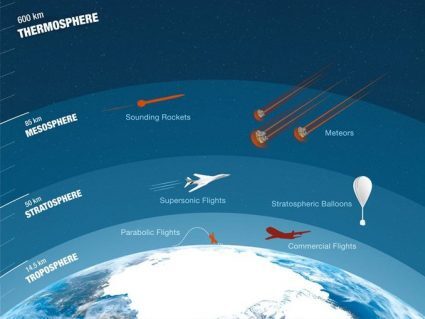
Main highlights of the stratosphere are: (1) The ozone layer absorbs harmful UV light (2) This causes temperature to rise (3) It contains 10% of air mass.
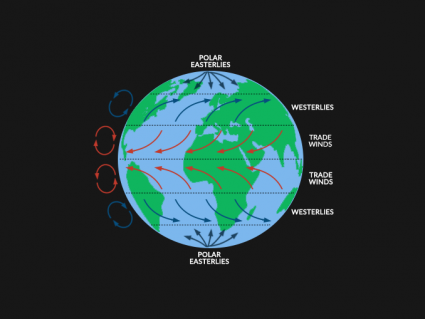
The Coriolis effect is the deflection of air due to Earth’s rotation. Air veers to the right in the northern hemisphere. And vice versa south of the equator.
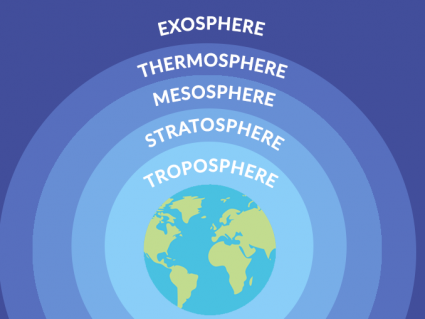
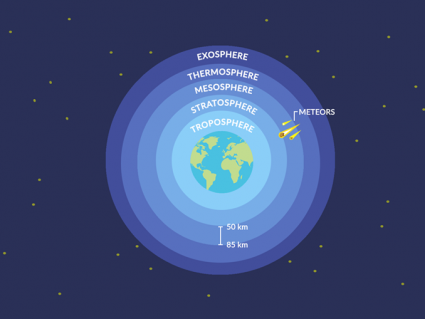
The exosphere is the upper part of Earth’s atmosphere. It starts at about 500 km and gradually extends into the vacuum of outer space at about 190,000 km.
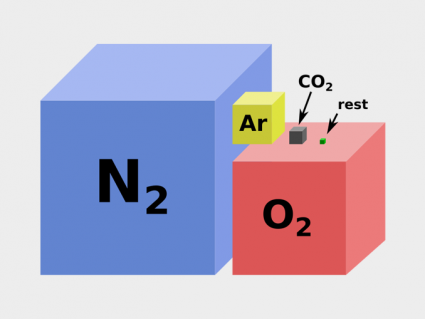
From largest to smallest, Earth’s atmosphere composition contains nitrogen, oxygen, argon, CO2 and trace gases. Water vapor is excluded from this total.
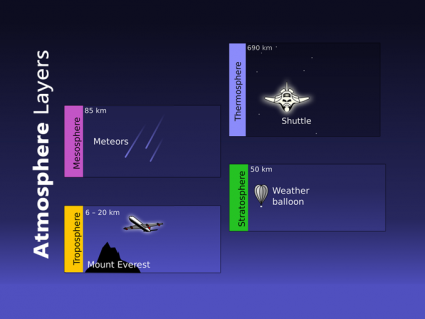
There are 4 primary layers of the atmosphere on Earth: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere. The ionosphere and exosphere are above those.
Highlights of the mesosphere include: (1) Air is very thin (2) It’s the coldest region of the atmosphere close to -100°C and (3) It’s where meteors burn up.