How Much Will Sea Level Rise?
What is sea level rise?
Sea level rise is a pressing global issue because of the gradual increase in the average height of the world’s oceans. This is primarily attributed to the melting of polar ice caps and the expansion of seawater due to rising temperatures.
The two major causes are:
- THERMAL EXPANSION: Thermal expansion of the oceans because heat makes water expand.
- GLACIER MELTING: Loss of land-based ice and glacier melting
As temperatures surge, sea levels rise with it. In fact, it’s projected to rise at an even greater rate this century. Let’s take a look at some of these global projections.
How much will sea levels rise?
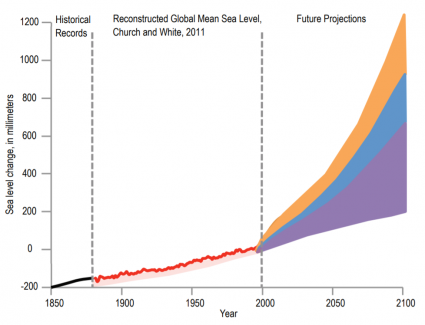
Since 1850, the global mean sea level has been steadily rising. In the chart below, the red line represents sea levels from observed tide gauge data. After the year 2000, sea-level rise is projected to spike.
The purple, blue, and orange areas show sea-level rise projections. But it has three levels of increase because of its uncertainty after 2050.
These climate models are derived from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, 2007)
How will glacier melt contribute to sea level rise
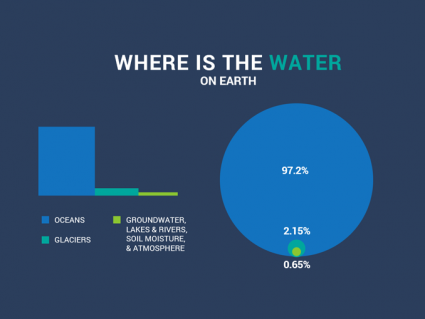
Earth holds about 326 million trillion gallons (326,000,000,000,000,000,000 gallons) of water. About 6,846,000,000,000,000,000 gallons (2.1%) of Earth’s water is in glaciers.
Glaciers are the second largest reservoir of water with most of them in Greenland and Antarctica. Currently, glaciers store about 24,060,000 cubic kilometers of water.
Glaciers fluctuate in water availability the most with ice ages and global warming. As temperatures surge, sea levels rise with it. This is because melting ice sheets and glaciers add to Earth’s total water volume.
Every year, sea ice grows in the winter. Then, it shrinks in the summer. But in March 2019, Arctic sea ice reached its annual maximum. It wasn’t a record low. But it continued a downward trend of sea ice maximums and minimums.
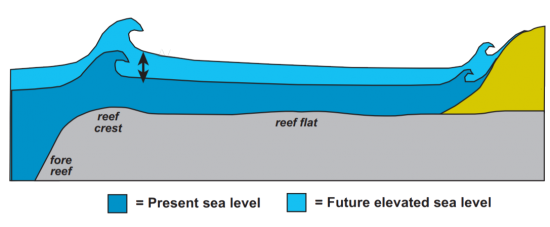
What is the future of sea level rise?
Scientists estimate the sea level will rise 32 to 68 inches by 2100. This rise in sea levels could swallow parts of coastal cities like Shanghai, Olympia, and New York.
How do we slow down the massive supply of water? First, we reverse deforestation to capture more carbon from the atmosphere.
Second, we reduce greenhouse gas emissions to help stabilize temperature. Finally, we all have to consider the environment in our daily lives.
How Much Will Sea Level Rise?
Sea level rise is an inevitable consequence of global warming. It’s a problem that places the entire world in danger. There are many solutions to this issue, but it will take a lot of effort to mitigate and reverse any damage done by sea level rise.
The urgency of addressing sea level rise is underscored by its potential to inundate coastal communities, disrupt ecosystems, and threaten vital infrastructure.
This global issue is all about making international cooperation and proactive measures essential in combating its effects.
We want to hear what you have to say about sea level rise! Please use the comment form below and let us know what your thoughts are.