How Much Water Is on Earth?
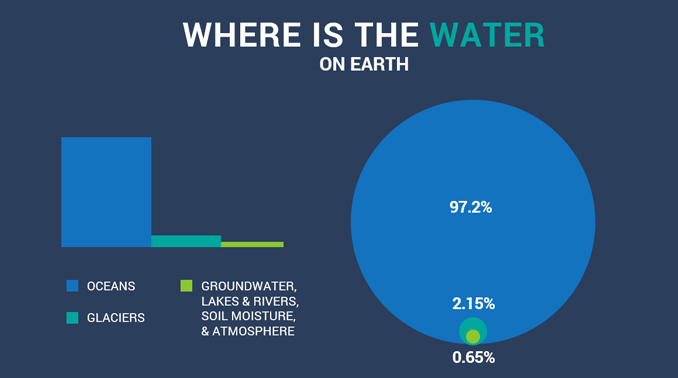
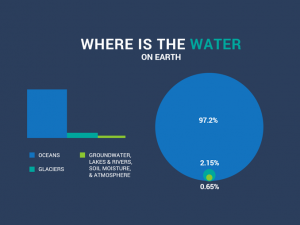
Where is the water on Earth?
Earth is unique because it has so much water. It’s in the ground, on the surface, in the air, and in our bodies.
Just how much water is there on Earth? About 71% of Earth’s surface is water. If you took all the water on Earth and put it into a ball, it would be about 860 miles wide.
Where is that water located? Is it saltwater or freshwater? How much water is in glaciers, groundwater, rivers, and lakes?
Let’s take a look at some of the interesting facts about global water distribution and volume on Earth.
Earth’s water by the numbers
The Earth holds about 326 million trillion gallons (326,000,000,000,000,000,000 gallons) of water [1].
If you crunch the numbers, here’s the percentage in global water distribution of all these sources of water.
| Source | Gallons | Percentage |
| Oceans | 316,872,000,000,000,000,000 | 97.2% |
| Glaciers | 6,846,000,000,000,000,000 | 2.1% |
| Groundwater | 2,119,000,000,000,000,000 | 0.65% |
| Lakes | 55,420,000,000,000,000 | 0.017% |
| Soil Moisture | 16,300,000,000,000,000 | 0.005% |
| Streams, wetlands and swamps | 3,260,000,000,000,000 | 0.001% |
| Total | 326,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 100% |
The table is a rough approximation of global water distribution as some water in the atmosphere as water vapor, permafrost, and biological water.
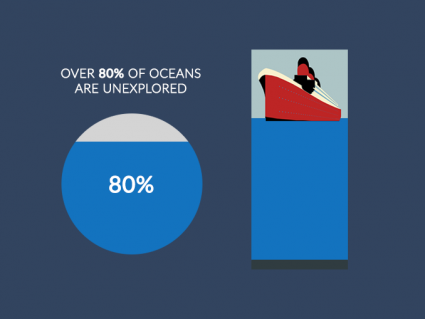
1. Oceans (97.2%)
Most of Earth is saltwater in oceans. About 97.2% of Earth’s surface water resides in oceans. There are 5 oceans that surround continents.
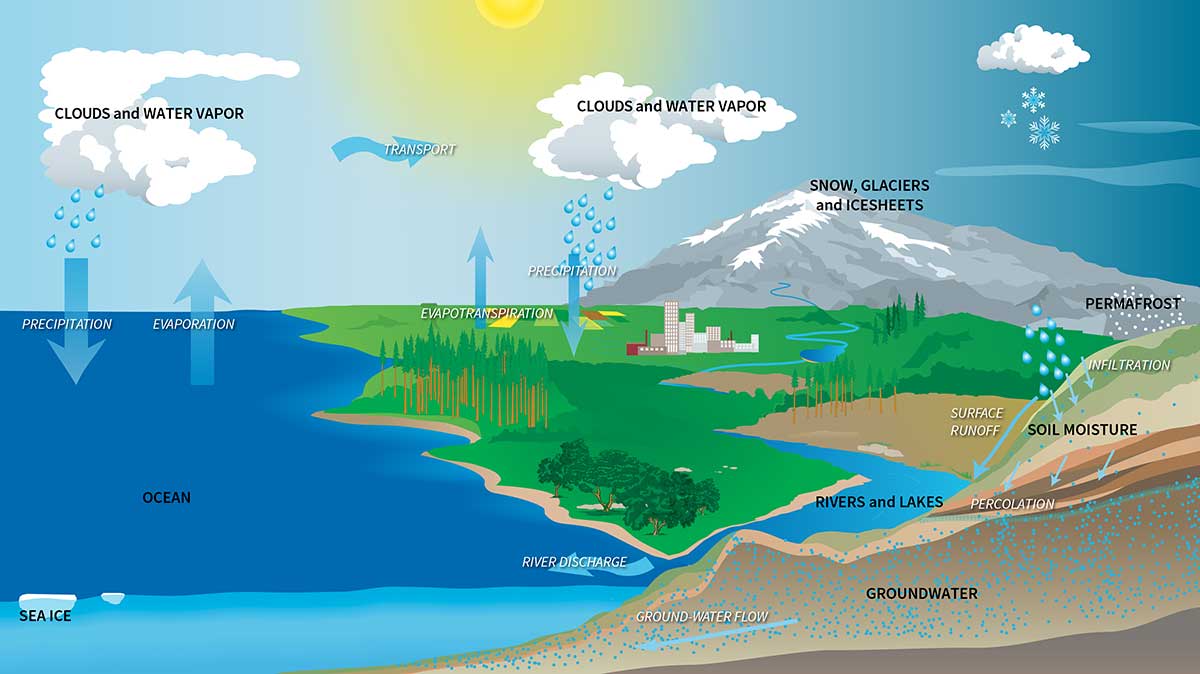
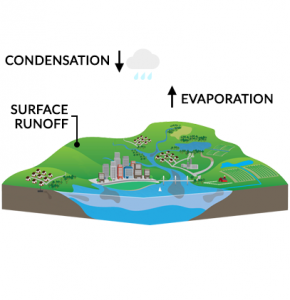
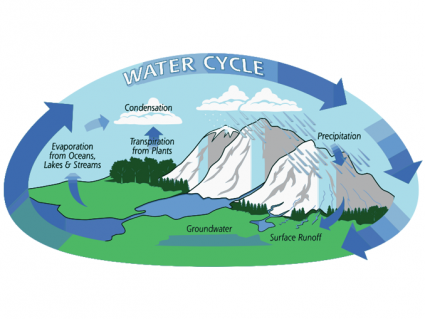
The average depth of oceans is 2.7 kilometers so water volume is about 1,338,000,000 cubic kilometers. Oceans are the foundation of the water cycle.
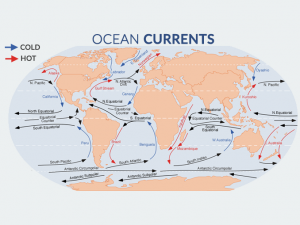
Water moves continuously in nature in three stages: evaporation, condensation, and surface runoff. Ocean currents are like giant conveyor belts moving huge amounts of water all the time.
2. Glaciers (2.1%)
About 2.1% of Earth’s water is in glaciers. Glaciers are the second largest reservoir of water with most of them in Greenland and Antarctica. Currently, glaciers store about 24,060,000 cubic kilometers of water.
Glaciers fluctuate in water availability the most with ice ages and global warming. As temperatures surge, sea levels rise with it.
This is because melting ice sheets and glaciers add to total water volume. Scientists estimate the sea level will rise 32 to 68 inches by 2100. This rise in sea levels could swallow parts of coastal cities like Shanghai, Olympia, and New York.
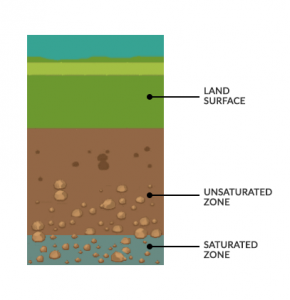
3. Groundwater (0.65%)
As a hidden source of water, we find groundwater everywhere. About 0.65% of the water on Earth is in groundwater stored in an aquifer.
There are two types of groundwater – saline and freshwater from groundwater. Fresh groundwater makes up about 45% of water in the ground. Whereas saline groundwater is about 55%.
Groundwater has more than 100 times the amount of freshwater than lakes and streams combined. In addition, groundwater is hard to get out of the ground, slow to recharge, and easily contaminated. That’s why groundwater is a delicate resource that we use as a rainy-day fund and draw in times of need.
4. Freshwater and Saline Lakes (0.017%)

Only 0.009% of water is stored in lakes. For example, the Great Lakes are sources of freshwater which consist of about 21% of freshwater lakes on Earth. Lake Baikal in Russia stores approximately the equivalent of all 5 Great Lakes.
Even though rainwater washes minerals and salts into rivers and lakes, they are mostly freshwater. This is because their minerals get washed away and transported to an outlet in the nearest ocean. So unlike salty oceans, lakes, and rivers constantly have the minerals washed away.
Saline lakes are landlocked bodies of water with a high concentration of salt (NaCl). Evaporation is the only way water exits from saline lakes. Saline lakes like the Caspian and Dead Seas only contain about 0.008% of Earth’s water.
5. Soil Moisture (0.005%)
Next, the soil is the uppermost layer that supports plant growth and agriculture. Soil moisture has only 0.005% of the global water distribution.
Soils are about half minerals, half-open space – all within the top few centimeters of the surface. It’s often mixed with organic material, sometimes called humus.
Soil texture describes particle size. For soil, it consists of sand, silt, and clay. Sand is the largest particle size. Silt is just sand, but smaller. Finally, clay has even smaller particles than silt.
6. Streams, wetlands, and swamps (0.001%)

Almost insignificant, streams, wetlands, and swamps hold only 0.001%. Finally, only 0.001% of water is in the form of vapor within the atmosphere or in living plants and animals.
For streams, everything upstream ends up downstream. Within a watershed, well-connected networks of tributaries catch precipitation in a watershed or catchment basin. They zig-zag all the way to a main body of water like a river or lake.
Wetlands are depressions on the land surface usually characteristic of specific vegetation. These types of habitats lay the foundation for biological diversity and resilient ecosystems.
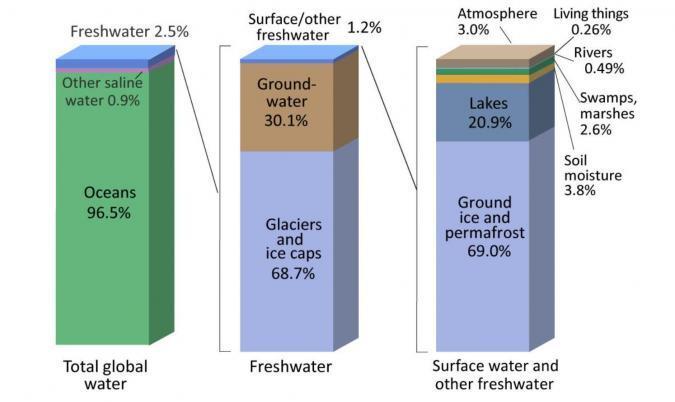
How much salt and freshwater are there?
If you compare saltwater vs freshwater, about 97.2% is not suitable for drinking because it has salt in it. If we sum up all the sources of freshwater, about 2.8% of water on Earth is freshwater.
Of that 2.8%, 99% of freshwater sources are either from glaciers or in an aquifer contained as groundwater. Just a minuscule amount (1%) are in freshwater lakes, streams, and in the atmosphere.
Glaciers store approximately 3/4 of Earth’s freshwater. This makes glaciers the largest reservoir of freshwater on Earth.
Finally, groundwater is the second-largest reservoir of freshwater on Earth. Groundwater varies on location. Fresh groundwater makes up about 45% of water in the ground. Whereas saline groundwater is about 55%.
How Much Water Is on Earth?
Earth has a surface area that’s 71% covered in water. This means that it’s no surprise that water plays a significant role in many aspects of our everyday lives.
Water is a necessity for life and it also contributes to the habitability of planets.
If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to let us know what’s on your mind. We would love to hear from you!
Sources
1. How Much of Earth’s Water is Stored in Glaciers? (USGS)
2. Global Water Volume (USGS)







this website is good keep the work up
this site is good very helpful
Let’s find out what truth of how many gallons of the Earth’s water is 1 percent and how long would it take to consume.
Very helpful. Great success!!
The total volume of water on Earth is about 1.386 billion cubic kilometers (km³) or 1.386 x 10^21 liters. Since there are 1,000 milliliters (mL) in a liter, we can convert this volume to milliliters… This means there is approximately 1.386 x 10^24 milliliters on Earth
How many milliliters of water are on Earth?
Thanks for your appreciation.
Very interesting and helpful information and contribution of author, still no one can’t change the useful chart of water “World freshwater resources” by Igor Shiklomanov in Peter H. Gleick(editor),1999.
Hi Kurt. The total amount of water on Earth is basically constant over time. It’s mostly determined by the water cycle. As water changes states, it stays in the hydrosphere… but as processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.
Is the total amount of water constant or can it fluctuate? If it can fluctuate, then by approximately how much and any sort of time frame. Thanks
Great information and graphics, thanks! Isn’t it amazing that almost 3/4 of the earth is water, yet we spend billions looking for tiny traces of past water on other planets?
So, the world, not counting the millions of square miles of desert, forest, and wasteland not producing emissions plus the 71% of the water covering the earth, where there are zero emissions except for a few steamships, etc., is causing global warming. Preposterous!
This is a wonderful resource for teachers! So glad I found it AND thank you for keeping it updated!