What is Earth’s Escape Velocity?
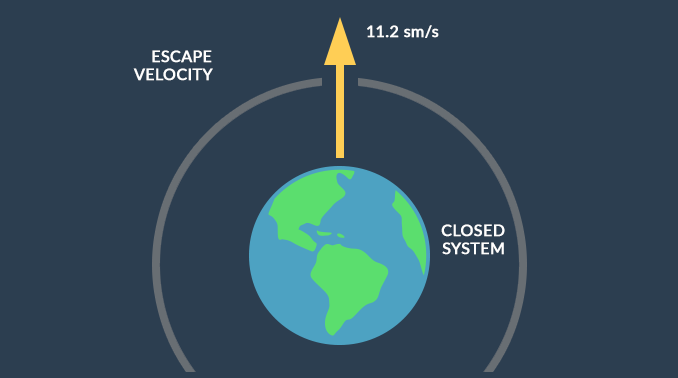
“The escape velocity of Earth is the speed at which a free object must travel to escape into space from a planet’s gravitational pull.”
Earth’s escape velocity is 11.186 km/s. So, if a free body travels at this speed, it can break away from Earth’s gravity into outer space.
Atmospheric composition is related to escape velocity. For example, Earth loses gases like hydrogen and helium because it isn’t large enough to hold onto them.
But Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus hold on tight to these gases because they are much bigger in size. In fact, their atmospheres are mostly these gases.
Earth exchanges little from and to the outside
Earth is nearly a closed system. We lose some hydrogen and helium from the atmosphere due to its escape velocity.
On top of that, we get the occasional meteor strike. But in general, Earth is a closed system because it doesn’t exchange matter from or to the outside.
Earth does exchange energy due to incoming solar radiation. The sun is always heating its surroundings. But little matter leaves or enters Earth.
The reason why Earth’s atmosphere composition is mostly nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide (CO2) is that their kinetic speed is slower than Earth’s escape velocity.
Remember that when carbon dioxide levels increase or decrease in the atmosphere, it doesn’t physically escape Earth. Rather oceans soak up CO2 like a sponge from biomass photosynthesis.
Venus has a similar escape velocity to Earth
Venus is a similar size to Earth. So, its escape velocity is very close at respectively 10.36 km/s.
But if you compare Earth’s atmosphere, Venus and Mars is about 95% CO2. Long ago, Earth may have had a similar atmosphere.
But it’s because biomass in Earth’s oceans that absorb CO2 removed large amounts from the atmosphere. It sequesters CO2 giving us a higher proportion of nitrogen and oxygen.
The absence of oceans and biomass on Venus and Mars means they retain an atmosphere heavy in carbon dioxide without oxygen.
Jupiter’s enormous mass means a high escape velocity
Planets like Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus are enormous in size. This has a direct correlation with their escape velocities.
Their escape velocities are high enough to retain gases like hydrogen and helium.
For example, Jupiter has an escape velocity of 59.5 km/s. If you compare this to Earth, the escape velocity is 5 times greater to escape the gravitational pull of Jupiter.
So, this is why Jupiter’s atmosphere mostly consists of hydrogen and helium. These gases haven’t been able to escape since Jupiter’s early formation.
What is Earth’s Escape Velocity?
Earth’s escape velocity is the speed that an object needs to be traveling in order to break free from Earth’s gravitational pull.
If an object has a lower escape velocity, then the object will not be able to break free from Earth’s gravitational pull.
Do you have any questions about Earth’s escape velocity? Please use the comment form below to get in touch with us.








wondering if year2024YR meteor is going fast enough to escape Earth’s gravitational pull.
It’s incorrect to say that Earth’s atmosphere is “mostly” nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide makes up 400 parts per million of the atmosphere. Argon, which didn’t make your list, makes up over 9000 parts per million of the atmosphere. It would be correct to say the atmosphere is mostly nitrogen or mostly nitrogen and oxygen but it’s incorrect to include carbon dioxide on that list.
Hi, this is incorrect. Mars’ mass is significantly lower than earth and venus. Mars escape velocity is 5.03km/s not 11.2!
Also, the first diagram states Earth escape velocity is 11.2 sm/s. You mean km/s