What is the Largest Desert in the World?
What is the biggest desert in the world? While the largest hot desert is the Sahara, Antarctica is the world’s coldest desert.

What is the biggest desert in the world? While the largest hot desert is the Sahara, Antarctica is the world’s coldest desert.

Mudflats are flat, muddy areas next to the sea or rivers. When the tide goes out, this exposes the wet, soft surfaces of a mudflat.

We’re hopping into the world of frogs to explore their incredible journey. In just four steps, we’ll uncover each stage of a frog lifecycle.

Nature interacts in some pretty interesting ways. Ecological relationships are like the friendships and rivalries in nature’s big community.

Ecosystems are like nature’s neighborhoods, where plants, animals, and living things work together. Learn about the types of ecosystems.

Tree rings are like a history book. They show us how old trees are and their environment like ring thickness, fire scars, and lopsided rings.

Plants do have some remarkable abilities that can seem extraordinary. Today, we’ll give you 15 examples of plants with superpowers.

Mangroves are trees that grow in coastal areas where the land meets the sea. They have unique roots in saltwater and help protect erosion.

Plastic takes a really long time to decompose. For some items like plastic bottles and drinking straws, it can take hundreds of years.
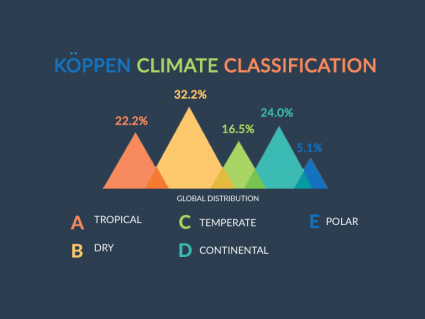
The Koppen climate classification catalogs Earth’s types of environments, which include tropical, dry, temperate, continental, and polar.
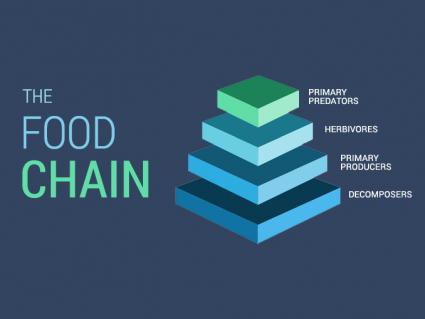
All living things rely on each other in the food chain. Energy transfers through living organisms from predators, herbivores, producers and decomposers.
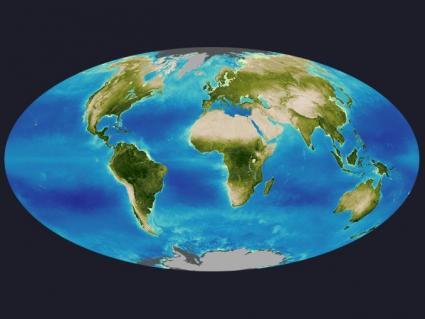
The biosphere is the layer of Earth where life exists. You, me, plants, insects bacteria and all living things on land, air and oceans are the biosphere.
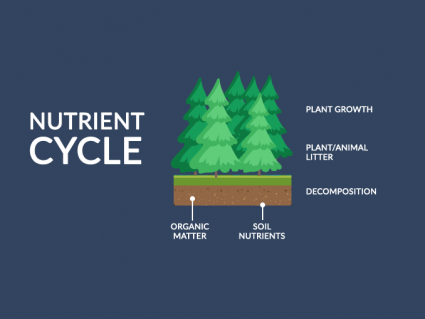
Food for thought, the nutrient cycle constantly exchanges inorganic and organic matter back and forth in the environment. It’s just recycled back and forth.
Biodiversity or “biological diversity” refers to the variety or genetic diversity of species in an ecosystem. Ecosystems rely on biodiversity for resiliency.
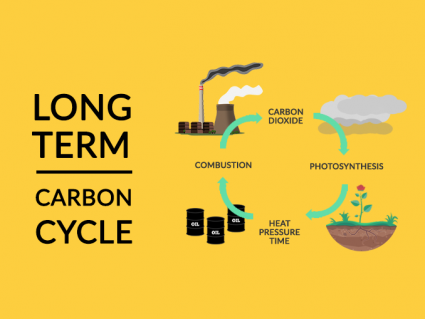
Carbon is re-purposed into fossil fuels in the long-term carbon cycle. The coal that we use today was produced millions of years ago from buried swamps.