4 Types of Soils
Soil is everywhere, under our feet, in gardens, and in the wild. But not all soils are the same. From silt to loam, learn the types of soils.

Soil is everywhere, under our feet, in gardens, and in the wild. But not all soils are the same. From silt to loam, learn the types of soils.

In this article, we’ll explain why soil is important. You’ll learn about its benefits in the environment and how it supports life on Earth.
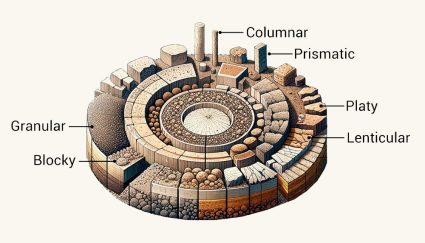
Soil is not just a single shape. Instead, it’s a mix of different shapes and soil structure. Let’s go on a journey into the ground beneath us.
Soil is a key part of our planet. They have many characteristics, each with unique features. Today, we’ll explore soil characteristics.

Terrace farming involves creating step-like fields in hilly areas, allowing farmers to grow crops on slopes and control soil erosion.

Soil horizons are layers in the soil, each with different characteristics. They form over time, due to various natural processes.

Strip cropping is a method where farmers grow different crops in narrow, long strips across a field that helps to control soil erosion.

The pedosphere is like the “skin of Earth”. Just like your skin, it has a thin outer surface. It also has pore spaces and dries out without enough moisture.
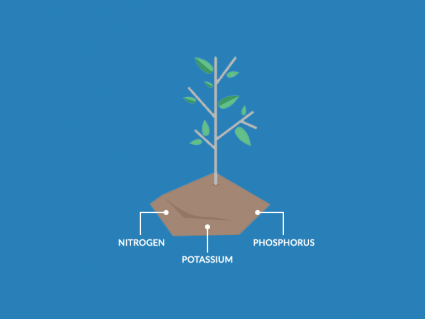
Plants mostly use water and carbon dioxide from the air to grow. But nutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) & potassium (K) are also key ingredients.

Soil formation is vital for food production and plant growth. Weathering is the process that breaks rock down into soils. Without it, soil wouldn’t exist.

Biological weathering can occur from mechanical force and chemical reactions such as through plants, bacteria, fungi, burrowing animals and living organisms
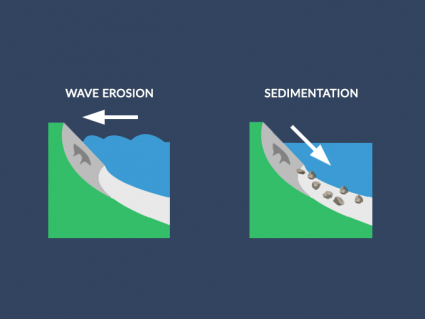
From the remarkable process of plates colliding and building mountains. They are only to be dismantled by mass wasting (weathering, erosion and transport).
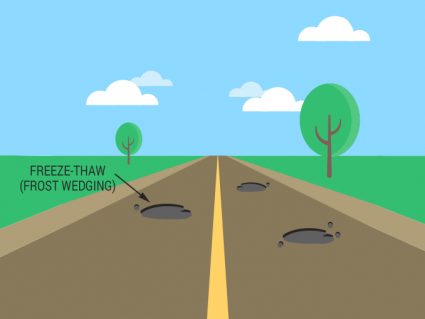
Mechanical weathering is the breakdown of rocks into sediments by physical means.This type of weathering does not alter the chemical composition of rocks.

Chemical weathering is the process of transforming a rock’s composition through chemical reactions (by dissolving or converting them into other minerals)