What’s the Difference Between Oceans and Seas?

Seas vs Oceans
Oceans are vast bodies of saltwater that cover about 71% of the Earth’s surface. They are the largest water bodies we have. Seas, on the other hand, are smaller and are partly surrounded by land.
While oceans are deep and open, seas are closer to coasts and can be thought of as parts of oceans. For example, the Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Atlantic Ocean, because it’s surrounded by Europe, Africa, and Asia.
At what point does a sea become an ocean?

You can easily reword this question the other way around. At what point does an ocean become a sea? There isn’t a specific point where a sea becomes an ocean. Instead, the difference is based on size and location.
Oceans are vast, open waters that stretch across thousands of miles. They are the largest bodies of saltwater on Earth. Seas, however, are smaller. They’re often surrounded by land or connected to oceans by narrow channels. The distinction is more about geography than strict size or depth criteria.
For example, the Caribbean Sea is considered a sea because it is largely surrounded by islands and continents, despite its large size. So, the terms “ocean” and “sea” reflect our understanding of Earth’s waters, shaped by both natural features and human definitions.
Which is deeper: the ocean or the sea?
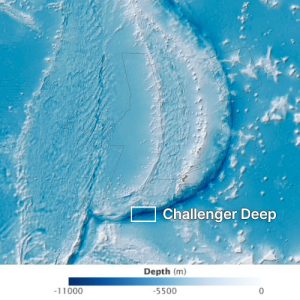
Generally, oceans are deeper than seas. Oceans have vast areas with depths reaching over 10,900 meters (35,000 feet), like the Mariana Trench. Seas are shallower, mostly because they are closer to land.
The average depth of the world’s oceans is about 3,682 meters (12,080 feet). In contrast, seas, such as the Mediterranean, have average depths of around 1,500 meters (4,900 feet). However, some seas can be quite deep, like the Caribbean Sea, which reaches depths of about 7,680 meters (25,220 feet).
Despite these exceptions, oceans hold the record for depth due to their vast, open basins. So, while seas can be deep, oceans go much deeper, holding the deepest points on Earth. See #6 in our 10 unsolved ocean mysteries.
Is it 7 seas or 7 oceans?
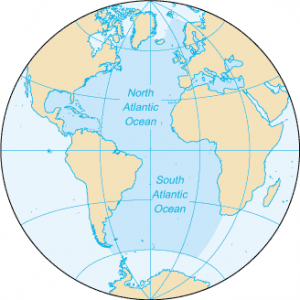
It’s neither. We use the term “Seven Seas” usually in historical context. A long time ago, the Seven Seas included regions like the Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, and others.
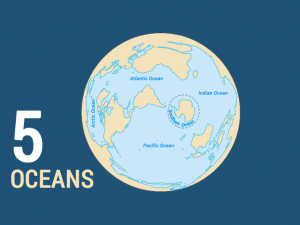
But this concept doesn’t accurately reflect modern geography. Currently, there are five oceans – the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Ocean.
There are over 50 seas around the world. This number includes large bodies of saltwater that are partially enclosed by land. The only exception is The Sargasso Sea because it’s defined by ocean currents in the North Atlantic.
What’s the Difference Between Oceans and Seas?
Both oceans and seas are part of the hydrosphere. But oceans are vast, open bodies of saltwater. They cover most of the Earth’s surface, making them the planet’s largest water bodies.
In contrast, seas are smaller and usually found where the land and ocean meet. They are often surrounded by land or partially enclosed by islands.
While oceans are deeper, with some of the deepest trenches in the world, seas tend to be shallower. They can have unique characteristics due to their closer proximity to land.
Do you have any questions about oceans and seas? Please add your comments in the form below and we’d be happy to get back to you.

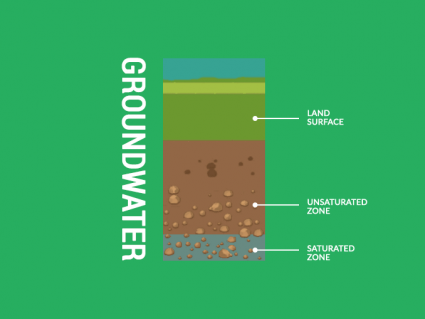

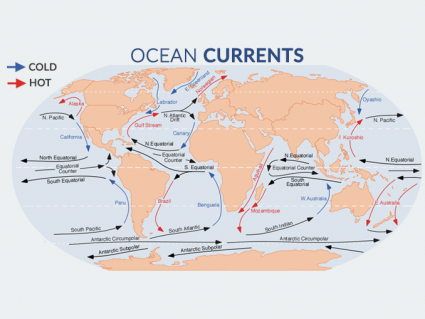


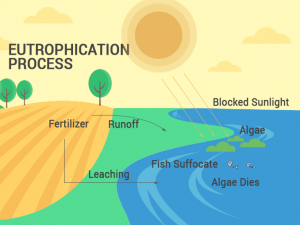



What kind of life form is in the Mariana Trench? How was the depth measured?