4 Types of Soils

Types of Soils
Soil is everywhere, under our feet, in gardens, and in the wild. But not all soils are the same. There are different types of soils, each with unique features.
Let’s explore these types and see how they vary. From sandy to clay, each soil has differences in nature. Understanding these can help us in gardening and farming.
1. Sandy Soils

Sandy soil is coarse and is characterized by its large particles. It allows water to drain quickly, resulting in quick drying.
Due to this rapid drainage, it struggles to retain water and essential nutrients. Nevertheless, its loose, non-sticky nature makes it easy to work with.
Moreover, it warms up quickly in spring, which is beneficial for early planting. However, the challenge lies in its limited moisture and nutrient retention, affecting plant growth.
2. Clay Soils

Clay soil is dense and heavy, with very small particles. When wet, it feels smooth and sticky. This soil type holds water well, often too well, leading to poor drainage.
It’s rich in nutrients and beneficial for plant growth. For example, crops like rice, wheat, and cotton grow well in clay soils due to their need for moisture retention.
However, its density makes it hard for roots to penetrate. In cold weather, clay soil becomes hard and compact. This becomes a challenge for gardening.
READ MORE: What Are Soil Horizons?
3. Silt Soils

Silt soil is fine and smooth, made of medium-sized particles. Its texture is softer than clay and sand.
Silt retains water well, but not as much as clay. It also holds nutrients better than sandy soil. This type of soil is fertile and good for agriculture, coupled with crop rotations.
However, it can become compact and hard to work with when wet. Because this compaction can lead to poor aeration and drainage, it can potentially hinder plant growth.
4. Loam Soils

Loam soil is a mix of sand, silt, and clay, bringing together the best parts of all types of soil. It’s fertile, drains well but it also holds moisture well.
Loam is easy to work with and provides good aeration for roots. This makes it a great option for most plants and gardening.
Because of these qualities, loam is often the top choice for gardeners and farmers. It supports healthy plant growth and makes maintaining gardens and crops easier.
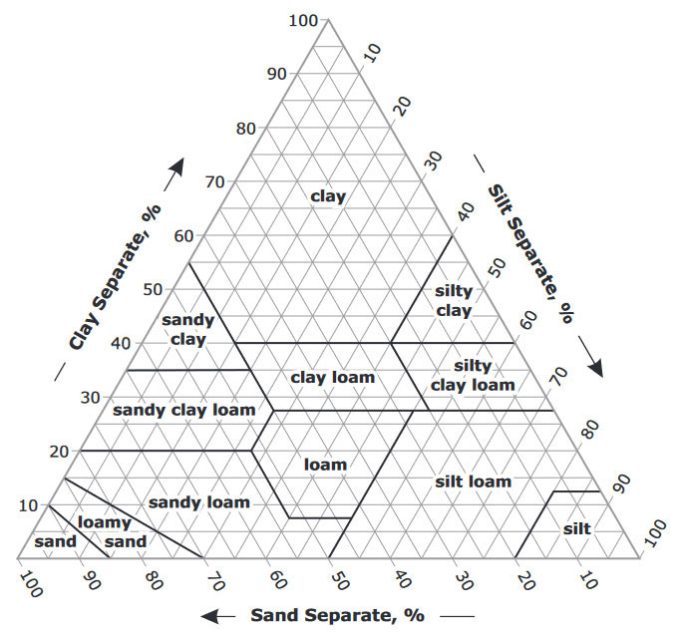
Soil Texture Pyramid
The soil texture pyramid is a tool used to classify soil types based on their particle sizes. It’s a triangular chart showing the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in various soils.
Each side of the pyramid represents one of these components. Where a soil’s composition falls within the triangle determines its texture class.
For example, a soil with equal parts of all three is classified as loam. This pyramid helps in understanding soil properties and guiding agricultural practices.
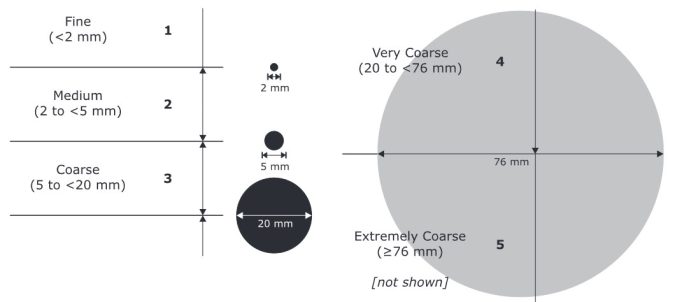
The Relationship Between Soil Coarseness
Soil types are like recipes. They mix clay, sand, silt, and organic matter in different amounts. Let’s break it down.
- Clay has tiny particles. It feels sticky when wet. It holds water well but drains slowly.
- Silt particles are medium-sized, smoother than sand, and hold water better than sand but not as well as clay.
- Sand has large particles. It feels gritty. Sand drains water fast but doesn’t hold nutrients well.
- Loam is the dream team. It has clay, sand, silt, and organic matter. It’s great for plants because it holds water and nutrients well and drains nicely.
So, the coarseness (fine, medium, coarse) tells us about the size of soil particles. Clay is fine; sand is coarse; silt is in the middle. Loam balances them all.
Types of Soils
Each soil type has its own unique qualities. Sandy soil drains fast but holds less water. Clay soil is rich in nutrients but hard for roots. Silt soil balances moisture and is great for certain crops. Loam combines all these benefits, making it the perfect soil for gardening and farming.
Understanding the characteristics of different types of soils is important for success. By choosing the right soil for specific plants, it can optimize growth, yield, and sustainability in agriculture.
RESOURCE: USDA Field Book for Soil Descriptions