What is Net Primary Productivity for Earth?
What is Net Primary Productivity?
Think of net primary productivity like a savings account. It’s how much carbon trees can store.
Then, you subtract the amount of carbon that trees respire. This gives you the net primary productivity.
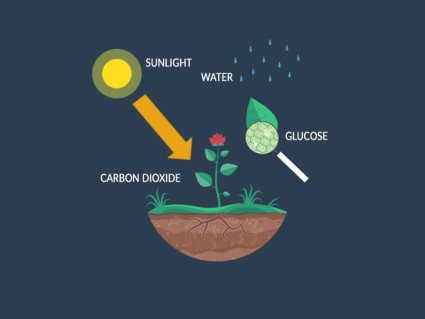
Net primary productivity is the net difference between photosynthesis and respiration in an ecosystem.
In other words, it’s how much carbon dioxide plants take in during photosynthesis minus how much they release during respiration.
Net primary productivity can only be negative if a plant’s cellular respiration rate is lower than its photosynthetic rate.
What are the most productive ecosystems?
Lush tropical rainforests are the most productive places on the planet. They also are some of the most biologically diverse places.
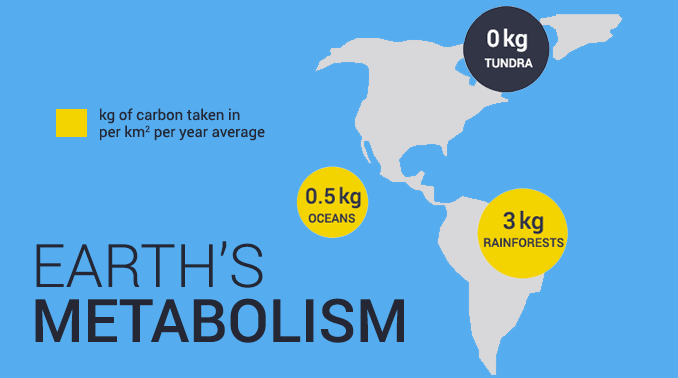
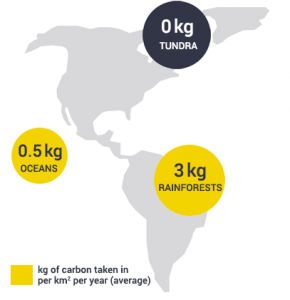
Throughout the whole year, rainforests in South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia have high net primary productivity.
Whereas countries in the mid-latitudes have high seasonal variations. For example, spring and summer exhibit high productivity in North America, Europe, and Russia.
But as winter comes, the rate at which plants absorb carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere dampens.
“Lush tropical rainforests are the most productive places on the planet. This mostly includes regions in South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia.”
What are the least productive ecosystems?

Some of the least productive ecosystems are:
- POLAR REGIONS: Polar regions and deserts are the least productive because both types of ecosystems experience little photosynthesis year-round.
- TUNDRAS: Not only are tundras cold in temperature, but they receive little rainfall. This is why high-latitude ecosystems have sparse vegetation so there is minimal energy flow.
- DESERTS: While Antarctica is a cold desert, hot deserts are covered in sand with little rainfall. They have hostile living conditions for plants and animals so net primary productivity is quite low.
Net Primary Productivity for Earth
The Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of Earth quantifies the annual amount of carbon dioxide removed from the atmosphere through photosynthesis by terrestrial plant life.
Overall, it represents a critical ecological measure that assesses the planet’s capacity to store carbon and sustain ecosystems through plant growth.
Do you have any questions about NPP? Please let us know in the comment section below and we’ll be happy to respond.



Sorry, not sure how net primary productivity has changed in Australia.
Hi could you explain how net primary productivity has changed in Australia from 1999-2008?
Don’t deserts have cactus?